Cell Biology Group
The Cell Biology Group recently described the identification of a novel protein, referred to as receptor-associated protein 80 (RAP80) or ubiquitin interaction motif-containing 1 (UIMC1). RAP80 is an acidic nuclear protein of 719 amino acids that contains two Cys-X2-Cys-X11-His-X3-Cys zinc finger-like motifs in its carboxyl-terminal half. RAP80 also contains two ubiquitin interacting motifs (UIMs) at its amino terminus. UIMs consist of a short sequence motif of about 20 residues reported to direct (multi)monoubiquitination of proteins that contain this motif. In addition, UIMs bind ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like motifs and may influence the activity of the protein. UIM-containing proteins play important roles in endocytosis, DNA-repair, (de)ubiquitination, replication and transcription. The Cell Biology Group demonstrated that the UIMs in RAP80 are functional and critical for the function of RAP80.
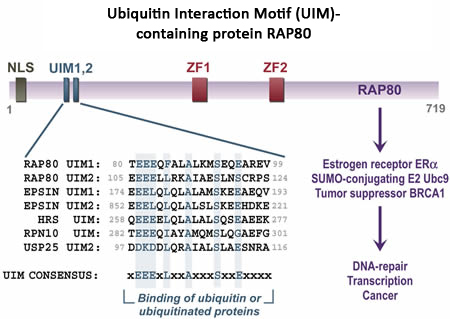
The Cell Biology group has established several important functions of RAP80. RAP80 interacts with several nuclear receptors, the retinoid-related testis-associated receptor (RTR), also known as germ cell nuclear factor GCNF or NR6A1, and the estrogen receptor a (ERα). However, it does not interact with ERβ or several other nuclear receptors. The interaction with ERα requires the presence of an agonist, such as estrogen, while antagonists do not induce the interaction. RAP80 influences the transcriptional activity of ERα suggesting that RAP80 is an important modulator of ERα. Additional studies have provided evidence for a role of RAP80 in DNA repair.
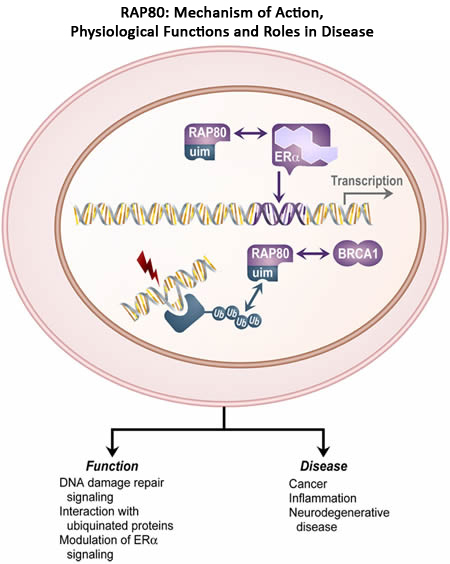
This research project has several goals.
- Understanding the role of RAP80 protein in the ERα signaling pathway
- Determining the role of RAP80 in DNA-repair
- Examining the role of RAP80 in cancer


