This glossary is intended to help understand terms related to Environmental Health Science.
Filter by First Letter:
A
- Acclimatization:
-
Physiological and behavioral adjustments to a change in environment.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Acid rain:
-
When sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) react in the atmosphere with water, it returns to earth as polluted rain, fog, or snow.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Acrylamide:
-
A chemical that can form in some foods during high-temperature cooking processes, such as frying, roasting, and baking.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Activated carbon filtration system:
-
A gas-phase air filter that removes gaseous pollutants using a material called a sorbent, such as activated carbon, to collect pollutants.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Adaptation:
-
An alteration in the behavior of an organism or species in order to become better suited towards its environment.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Adaptation research:
-
Scientific investigation that focuses on specific policies and actions to reduce the vulnerability of humans, communities, and living systems.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Adaptive capacity:
-
The ability of a system or organism to adjust to change, moderate potential damages, take advantage of opportunities, or to cope with the consequences.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Aeroallergens:
-
Airborne substances such as pollen or spores that can cause an allergic response.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Aerosol:
-
Fine solid or liquid airborne particles, with a typical size between a few nanometers (nm) and 10 micrometers (μm) that reside in the atmosphere for at least several hours.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Aggregate risk:
-
The risk posed by the combination of exposure to multiple agents or stressors over time.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Agricultural health:
-
The study of environmental, occupational, dietary, and genetic factors on the health of farmers, farm families, and others who work with and are exposed to agricultural chemicals.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Airborne disease:
-
Illness transmitted when droplets, aerosols, and spores containing pathogens are expelled into the air and then inhaled by others.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Air pollution:
-
Degradation of indoor or outdoor air quality by introduction of any chemical, physical, or biological agent into the atmosphere.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Algae:
-
Photosynthetic organisms forming the base of the food chain in freshwater and marine ecosystems.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Allergens:
-
A substance that causes an allergic reaction.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Allergic reaction:
-
An abnormal physiological response by a sensitive person to a chemical or physical stimuli that causes no response in nonsensitive individuals.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Allergy:
-
An abnormal reaction of the body to a substance typically introduced by inhalation, ingestion, injection, or skin contact.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Aloe vera:
-
A succulent plant widely used in alternative medicine.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Anemia:
-
A condition in which the blood does not carry enough oxygen to the rest of the body; the most common cause of anemia is not having enough iron.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Animal reservoir:
-
An animal in which an infectious agent lives, grows, and multiplies.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Antibiotic:
-
A chemical originally produced by a microorganism, which inhibits or prevents the growth of another microorganism. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Anxiety:
-
A mental health disorder that produces fear, worry, and a constant feeling of being overwhelmed. It is characterized by excessive, persistent, and unrealistic worry about everyday things.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Applied research:
-
Scientific investigation undertaken to acquire new knowledge that is directed primarily towards a specific, practical aim or objective.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Aquaculture:
-
Also known as fish or shellfish farming, seafood grows in controlled waters for commercial or recreational use.
Source: NLM/NIEHS EHS glossary
- Aquifers:
-
An underground level or permeable rock, sand, or gravel saturated by groundwater.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Arsenic:
-
A grayish-white element having a metallic luster, vaporizing when heated, and forming poisonous compounds.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Asbestos:
-
Any of several minerals (as chrysotile) that readily separate into long flexible fibers that have been used especially formerly as fireproof insulating materials.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Assays:
-
A qualitative or quantitative test for a particular chemical effect.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Asthma:
-
A chronic lung disease characterized by episodes of airway narrowing and obstruction, causing wheezing, coughing, chest tightness and shortness of breath.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Atomic nuclei:
-
The small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Autoimmune diseases:
-
Over 80 different conditions in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy body cells. They likely result from genetic and environmental factor interactions.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
B
- Bacteria:
-
Single-celled microorganisms that lack a nuclear membrane, are metabolically active, and divide by binary fission. Medically they are a major cause of disease.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Basic research:
-
Scientific investigation directed towards a greater knowledge or understanding of the fundamental aspects of phenomena and observable facts.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Barometer:
-
An instrument for determining the pressure of the atmosphere.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Behavioral health:
-
The promotion of mental health, resilience, and wellbeing; the treatment of mental and substance use disorders; and the support of those who experience and are in recovery from these conditions, along with their families and communities.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Behavioral and social sciences research:
-
Scientific investigation that has a major and explicit focus on the understanding of behavioral or social processes, or on the use of such processes to predict or influence health outcomes or health risk factors.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Bioaccumulate:
-
Accumulation of substances in living organisms as they take in contaminated air, water, or food; occurs when a substance is absorbed faster than it can be excreted.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Biofuels:
-
Derived from biological materials, such as algae and plants, that can be regenerated. Distinguished from fossil fuels, which are nonrenewable. Examples include ethanol, methanol, and biodiesel.
Source: EPA.gov
- Biologics:
-
The immunization vaccines, antigens, anti-toxins, and other preparations made from living organisms and their products intended for use in diagnosing, immunizing, and treating humans and animals or in related research.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Biomagnify:
-
The process by which a compound (such as a pollutant or pesticide) increases its concentration in the tissues of organisms as it travels up the food chain.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Biotechnology:
-
An applied science that uses living organisms like plants and bacteria to produce products for healthcare, energy, and environmental safety.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Birth outcome:
-
Results of conception and ensuing pregnancy, such as gestational age and infant birth weight.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Black lung disease:
-
Coal worker's pneumoconiosis, also known as black lung disease, results from breathing in dust from coal, graphite, or manmade carbon over a long period.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Bronchitis:
-
An inflammation of the bronchial linings causing a persistent cough, copious amounts of sputum, and involuntary muscle spasms that constrict the airways.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Buckyballs:
-
Is a spherical fullerene molecule with the formula C60.
Source: Wikipedia
C
- Cadmium:
-
A soft, silver-white metal in its pure state used in the production of nickel-cadmium batteries; in metal plating, plastics, and synthetics; for alloys and other miscellaneous uses.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Cancer:
-
A disease caused by an uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in a part of the body.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Carbon cycle:
-
The process by which living things absorb carbon from the atmosphere, sediments and soil, or food. To complete the cycle, carbon returns to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide or methane by respiration, combustion, or decay.
Source: EPA.gov
- Carbon dioxide (CO2):
-
A colorless, odorless, greenhouse gas composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms produced by combustion, respiration, and organic decomposition.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Carcinogen:
-
Any substance that is capable of inducing the production of cancer.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Cardiovascular:
-
Pertaining to the heart (cardio) and the blood vessels (vascular). The cardiovascular system includes: arteries, arterioles, capillaries.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Cataracts:
-
A clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision; cataracts are very common in older people.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Chlorides:
-
Compounds of chlorine with another element or group.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
-
A group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Citizen science:
-
A collaborative approach to research that involves the public, not just as subjects but as direct collaborators and partners in designing and conducting research.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Coastal ocean:
-
Area near the shoreline from the outer edge of the continental margin that encompasses a broad range of saltwater ecosystems, from estuaries and coral reefs, to rocky shores and mangrove forests.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Coastal wetlands:
-
Saltwater and freshwater wetlands located within coastal watersheds, specifically USGS 8-digit hydrologic unit watersheds which drain into the Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, or Gulf of Mexico
Source: University of California, Davis
- Cognitive disorder:
-
A condition affecting development of general intellectual functioning,such as reasoning, planning, judgment, abstract thinking, academic learning, and experiential learning.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Cohort:
-
A well-defined group of people who have had a common experience or exposure, who are then followed up for the incidence of new diseases or events.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Co-infection:
-
The simultaneous occurrence of infections by two or more infectious (pathogenic or non-pathogenic) agents and includes both acute and chronic infections by viruses, bacteria, parasites, and/or other microorganisms.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Cold wave:
-
A rapid fall in temperature within 24 hours and the persistence of abnormally low temperatures for an extended period.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Coliform bacteria:
-
Bacteria that are always present in the digestive tracts of animals, including humans, and are found in their wastes; also found in plant and soil material.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Communication research:
-
At its broadest, communication research is concerned with identifying, exploring, and measuring the factors that surround communication and dissemination, in any form and regarding any topic; often from a theory-driven perspective, but increasingly with empirically-grounded methods.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Comorbidity:
-
The condition of having two or more diseases or medical conditions at the same time.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Conceptual site model:
-
The conceptual site model is a written and/or illustrative representation of the physical, chemical and biological processes that control the transport, migration and actual/potential impacts of contamination (in soil, air, ground water, surface water and/or sediments) to human and/or ecological receptors.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Consumer confidence report (CCR):
-
An annual water quality report or a drinking water quality report, that provides information on your local drinking water quality.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Corrosion:
-
The action, process, or effect of corroding, which is to wear away gradually usually by chemical action.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Cost prediction:
-
Research study focusing on health-related costs or other economic impacts such as loss of livelihood.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Creosote:
-
A wood preservative derived from the distillation of tar from wood or coal.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Crustaceans:
-
Any of a large class of mostly aquatic arthropods that include lobsters, shrimp, crabs, wood lice, water fleas, and barnacles.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Cryptosporidium:
-
Cryptosporidium A one-celled (protozoan) parasite that infects the intestines of people and animals. Cryptosporidiosis is an infection caused by Cryptosporidium.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Crystalline silica:
-
A basic component of soil, sand, granite, and many other minerals; may become particles small enough to inhale when workers chip, cut, drill, or grind objects that contain it.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Cumulative health effects:
-
The overall health impacts of all stressors, exposure routes, and/or agents over time.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Curing:
-
To add preservatives and flavors (salt, sugar, nitrates) to meat in order to improve flavor, color, and shelf life.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Cyanobacteria:
-
A photosynthetic group of bacteria that are functionally similar to algae.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
D
- Dander:
-
Tiny scales from hair, feathers, or skin that may cause allergies and affect indoor air quality; household pets are sources of saliva and animal dander.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
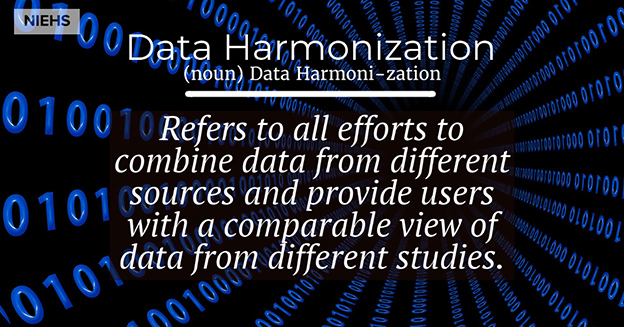
- Data integration:
-
The technical process of aggregating data from a variety of sources and providing users with a unified view of them.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- DDT:
-
A colorless odorless water-insoluble insecticide.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Degree days:
-
A unit of measurement referring to a measure of the outdoor mean temperature recorded for a location as compared to a standard temperature over a day or period of days that indicates levels of energy needed for heating during that time
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Demographic:
-
The description or distribution of the characteristics of a population or individual such as age, gender, and income.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Dengue fever:
-
An infectious disease carried by mosquitoes and caused by any of four related dengue viruses.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Dermatological outcome:
-
Any impact that affects the development or growth of hair, nails, and skin.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Desert:
-
Arid land with usually sparse vegetation.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Developmental outcome:
-
The result of an impact on the growth of a human from conception to maturity.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Diabetes:
-
Metabolic condition caused by changes in blood glucose intolerance and insulin sensitivity.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Diethylstilbestrol (DES):
-
A synthetic form of the female hormone estrogen, linked to a type of cancer of the cervix and vagina, that was prescribed to pregnant women between 1940 and 1971 to prevent miscarriage and related pregnancy complications.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Dioxin:
-
A highly toxic compound produced as a byproduct in some manufacturing processes, notably herbicide production and paper bleaching. It is a serious and persistent environmental pollutant.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Disaster:
-
An occurrence of a natural catastrophe, technological accident, or human-caused event that has resulted in severe property damage, deaths, and/or multiple injuries.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Disaster preparedness:
-
The continuous cycle of planning, organizing, training, equipping, exercising, evaluating, and taking corrective action in an effort to ensure effective coordination during incident response.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Disaster recovery:
-
The process of improving individual, family, and community resiliency after the occurrence of a disaster. Recovery entails restoration of structures, systems, and services; ability of individuals and families to rebound from their losses and sustain their physical, social, economic, mental, emotional, and spiritual well-being.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Disaster research response:
-
A multidisciplinary research approach of scientists from social, behavioral, physical, and health sciences to understand the factors that influence disasters, disaster response mechanisms, and long term health consequences of disasters.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Disaster response:
-
Activities that address the short-term, direct effects of an extreme event. Response includes immediate actions to save lives, protect property, and meet basic human needs.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Disaster risk reduction:
-
The process of using systematic efforts to analyze and manage the causal factors of disasters and extreme events, including through reduced exposure to health hazards, lessened vulnerability, and improved resilience to natural disasters through strategic measures employed for anticipating future disaster risk.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Disease burden:
-
The impact of a health problem as measured by mortality, morbidity, financial cost, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Domoic acid poisoning:
-
A neurotoxin contained in some fish and shellfish; exposure to this compound affects the brain, causing seizures and possibly death.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Dredges:
-
A tool usually in the form of an oblong iron frame with an attached bag net used especially for gathering fish and shellfish.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Drought:
-
A prolonged period of dry weather caused by a lack of precipitation that results in a serious water shortage for some activity, population, or ecological system.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Drywell:
-
A hole in the ground filled with gravel or rubble to receive drainage water and allow it to percolate away.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Dust storm:
-
A hole in the ground filled with gravel or rubble to receive drainage water and allow it to percolate away.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
E
- E. coli:
-
A type of bacteria (Escherichia coli) that lives in intestines; most types of E. coli are harmless, but some types can cause diarrhea.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Ecosystem:
-
All the living things in a particular area as well as components of the physical environment with which they interact, such as air, soil, water, and sunlight.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Ecosystem services:
-
The benefits or "services" of an ecosystem to human life, such as clean water and the decomposition of organic matter.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Electrolyte imbalance:
-
Minerals (such as sodium, calcium, and potassium) in the body have an electric charge. Electrolyte imbalance is when concentrations of these minerals are too high or too low.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Electromagnetic fields:
-
Invisible areas of energy that are associated with the use of electrical power and various forms of natural and man-made lighting.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Emissions:
-
A discharge of pollutants into the environment; generally used in regard to discharges into the air.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Emphysema:
-
A chronic disease of the lungs in which the lung tissue becomes destroyed and the affected area is unable to participate in the transfer of oxygen to the body.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Encephalitis:
-
An inflammation of the brain caused by a viral (usually) infection or a bacterial infection.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Endemic:
-
The state of having a disease that is constantly present in a certain geographic area or in a certain group of people.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Endocrine:
-
Relating to or denoting glands which secrete hormones or other products directly into the blood.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Endocrine disruptor:
-
Chemicals that can interfere with hormones at certain doses.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Endocrine gland:
-
A structure in the body that produces hormones which are then secreted directly into the bloodstream.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Endometriosis:
-
The presence and growth of functioning endometrial tissue in places other than the uterus that often results in severe pain and infertility.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Environment:
-
The air, water, and land, and the relationship that exists between them and all living things, including plants, humans, and other animals.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Environmental health:
-
The science of identifying and understanding the impacts of environmental exposures to hazardous physical, chemical, and biological agents in air, water, soil, food, as well as social stressors that may adversely affect human health. The goal of environmental health is to prevent human injury and illness and promote well-being.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Epidemiology:
-
The scientific field of study used to determine the distribution and determinants of health related outcomes and events in a specified population.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
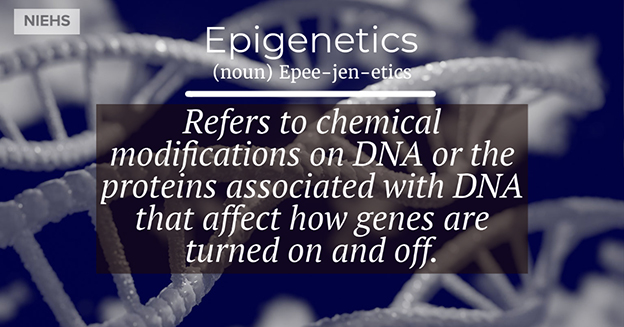
- Epigenesis:
-
Development of a plant or animal from an egg or spore through a series of processes in which unorganized cell masses differentiate into organs and organ systems.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Essential oils:
-
Concentrated plant extracts that retain the natural smell and flavor of their source and are obtained through mechanical pressing or distillation.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Eutrophication:
-
Over-enrichment of water by nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. It is on of the leading causes of water quality impairment. The two most acute symptoms are hypoxia, or oxygen depletion, and harmful algal blooms.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Excavation:
-
A cavity formed by cutting, digging, or scooping.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Experimental design:
-
A study that can test cause and effect relationships between subjects under specific treatment conditions.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Exposome:
-
Everything the body is exposed to throughout life.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Exposure:
-
Contact between a person and one or more biological, chemical, physical or social stressors. Contact may occur in a single instance or repeatedly over time, and may occur in one location or over a wider geographic area.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Exposure assessment:
-
An evaluation process used to estimate or measure the magnitude, frequency, duration, and route of exposure to an agent, along with the number and characteristics of the population exposed.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Exposure pathway:
-
The link between an environmental release or source to the point where a person might come into contact with, or be exposed either by inhalation, ingestion, or direct contact, to an environmental agent.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Exposure science:
-
The study of our contact, such as by swallowing, breathing, or touching, with environmental factors and their effects on the human body.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Extreme temperatures:
-
Temperature variations above (extreme heat) or below (extreme cold) normal conditions.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Extreme weather:
-
Unexpected, unusual, unpredictable severe or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Extreme weather events:
-
Unexpected, unusual, unpredictable, severe, or unseasonal weather; typically defined as occurring in the highest and lowest 5% of the historical distribution of similar weather parameters.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
F
- Fatty tissue (adipose tissue):
-
The fat storage tissue in the bodies of animals. It is primarily a food storage mechanism but also provides thermal insulation and protects internal organs from external physical damage.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Feedstock:
-
Raw material, usually plant or agricultural waste, that can be converted into fuel or energy.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Fertilizers:
-
A substance that adds inorganic or organic plant nutrients to soil and improves its ability to grow crops, trees, or other vegetation.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Fiberglass:
-
A composite material of glass fibers in resin; used in nail wrap applications to brace natural nails or artificial tips.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Fine particulate matter (PM 2.5):
-
A complex air pollutant mixture that can include metals, organic chemicals, acid droplets, and soil or dust particles.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Fission:
-
The splitting of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of large amounts of energy.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Five-G (5G):
-
The fifth version of a product or system. 5G is the term used to describe the next-generation of mobile networks beyond LTE mobile networks.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Flame retardants:
-
Chemicals that are applied to materials to prevent the start or slow the growth of fire.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Flood:
-
An overflow of water that submerges usually dry land. Floods are often caused by heavy rainfall, rapid snowmelt, or a storm surge from a tropical cyclone or tsunami in coastal areas.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Foodborne illness/disease:
-
An illness or disease caused by ingestion of foods or drinks contaminated with biological or chemical toxins or pathogens.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Food security:
-
A state that prevails when people have secure access to sufficient amounts of safe food for normal growth, development, and an active and healthy life.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Forest:
-
A large area dominated by trees.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Framework:
-
An underlying structure or model to support our collective research efforts.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Freshwater:
-
Any naturally occurring water except seawater and brackish water including a lake, river, river basin, and a riverine.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Formaldehyde:
-
A colorless, flammable, strong-smelling chemical widely used to make home building products.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Fossil fuels:
-
A fuel (such as coal, oil, or natural gas) formed in the earth from plant or animal remains; fossil fuels are the nation's principal source of electricity; they cannot be replenished once they are extracted and burned.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Fossil fuels:
-
A fuel (such as coal, oil, or natural gas) formed in the earth from plant or animal remains; fossil fuels are the nation's principal source of electricity; they cannot be replenished once they are extracted and burned.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Fumigants:
-
A pesticide used to control or destroy fungi on food or grain crops.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Fungi:
-
A plant-like organism that does not make chlorophyll.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Furans:
-
A flammable liquid chemical compound that is obtained from wood oils of pines or made synthetically and is used especially in organic synthesis; also: any of various derivatives of furan.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
G
- Gamma rays:
-
Radiant electromagnetic energy of a very short wavelength capable of penetrating most substances; it is given off by radioactive substances and during fission and fusion reactions.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Gastrointestinal system:
-
The organ system which includes the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. It also includes the salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, which make digestive juices and enzymes that help the body digest food and liquids.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Geothermal energy:
-
Heat energy generated by the earth's interior.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Ginkgo biloba:
-
One of the oldest living tree species in the world, has a long history in traditional Chinese medicine.
Source: National Institutes of Health
- Global mean surface temperature:
-
The global average of combined land surface air and sea surface temperatures over a certain period of time.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Grantee:
-
The recipient of a grant, scholarship or fellowship, or some other funding source from NIEHS or other NIH institute.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Grassland:
-
A large open area of country covered with grass, especially one used for grazing including grasslands, savanna, prairie, moorlands, and lowlands.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Greenhouse gases:
-
Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. The main greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Growing degree days:
-
A measure of the outdoor mean temperature recorded for a location as compared to a standard temperature over a day or period of days that indicates levels of energy needed for cooling during that time.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Groundwater:
-
The water found below the surface of the land and contained in the pore spaces of saturated rock, sand, or gravel; the source of water found in wells and springs.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Gynecomastia:
-
A condition of overdevelopment or enlargement of breast tissue in men or boys, often during puberty. But it is also seen in newborn babies and in men as they age.
Source: EPA.gov
H
- Hair dye:
-
Hair Dyes, which changes the hair color, contain many different chemicals that may act as carcinogens or endocrine disruptors.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Hantavirus:
-
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, a rare but deadly viral infection spread by mice and rats.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Harmful algal bloom (HAB):
-
Toxic blooms created by a small subset of naturally occurring microscopic or larger, plant-like cyanobacteria or algal species, including diatoms and dinoflagellates. Under certain conditions, such as in excess nutrients, sunlight, and slow moving water, these species can form large masses, or “blooms.” The algae in these blooms is ultimately consumed (typically by zooplankton) and recycled as fecal pellets, or dies naturally and sinks. Bacteria decompose these algal remains, a process which consumes dissolved oxygen contained in the water. When the rate of oxygen consumption in aquatic environments exceeds resupply, oxygen concentrations can quickly decline to levels insufficient to sustain most animal life, producing hypoxic conditions.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Health:
-
A state of physical, mental and social well-being, and not just the absence of disease.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Health effects research:
-
Scientific investigation that focuses on the influences of exposures on health outcomes, including spatial and temporal scales, pathways, and mechanisms, and risks at specific times of vulnerability across the lifespan, as well as to special populations including children, older adults, women, pregnant women, differently abled persons, and others.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Health hazard:
-
Chemical, physical, or biological factors in our environment that can have negative impacts on our short- or long-term health.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Health systems research:
-
Scientific investigation that addresses questions concerning the performance of a health system as a whole in the public or private sector. Areas of investigation include health financing, governance, and policy; structure, planning, and management; and service delivery, referral, and quality of care.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Healthcare sector:
-
The entierty of providing medical care, manufacturing medical equipment or drugs, providing medical insurance, or otherwise facilitating the provision of healthcare to patients.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Healthcare services:
-
Healthcare professionals providing the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of any human disease or the assessment or care of the health of human beings.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Heat wave:
-
A period of abnormally hot weather often combined with excessive humidity lasting two or more days.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Heat stress/heat related illness:
-
A heat related illness caused by prolonged exposure to extreme heat that can result in conditions such as heat stroke, heat exhaustion, heat cramps, or heat rashes.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Hepatic system:
-
A series of veins that carry blood from the capillaries of the stomach, intestine, spleen, and pancreas to capillaries in the liver. It is part of the body’s filtration system and its main function is to deliver de-oxygenated blood to the liver to be detoxified further before it returns to the heart. It consists of the hepatic portal vein, inferior mesenteric vein, superior mesenteric vein, and the gastrosplenic vein. br> Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Hormone:
-
A chemical substance in animals secreted by the endocrine gland, used to regulate metabolic activity.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
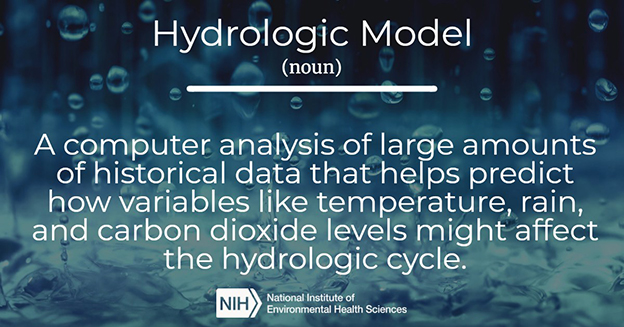
- Hydrologic model:
-
A computer analysis of large amounts of historical data that helps predict how variables like temperature, rain, and carbon dioxide levels might affect the hydrologic cycle.
Source: University of California, Davis
- Hypertension:
-
A common condition that develops when blood flows through the arteries at higher-than-normal pressures. Also called high blood pressure.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Hyperthermia:
-
Abnormally high body temperature caused by a failure of the heat-regulating mechanisms of the body to deal with the heat coming from the environment.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Hypoallergenic:
-
Having little likelihood of causing an allergic response.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Hypothermia:
-
Unusually low body temperature that causes a rapid, progressive mental and physical collapse.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
I
- Implementation science:
-
Scientific investigation of methods to promote the adoption and integration of evidence-based practices, interventions, and policies into regular use.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Incidence:
-
The proportion of a population or rate of persons who develop a condition during a specific time period.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Incomplete combustion:
-
The incomplete burning of natural gas, gasoline, liquefied petroleum gas, oil, diesel fuel, kerosene, coal, charcoal, or wood that produces carbon monoxide.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Indigenous peoples:
-
Communities that live within, or are attached to, geographically distinct traditional habitats or ancestral territories and who identify themselves as being part of a distinct cultural group that maintains a cultural and social identity distinct from the mainstream or dominant culture.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Indoor environment:
-
An area and its contents situated inside a house, building, school, or other structure.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Infectious disease:
-
A characterization of a disease indicating it can be transmitted typically by an infectious agent between organisms.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Inflammation:
-
The primary host response to infection. Also an essential component of the response to most other forms of injury.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Infrastructure:
-
The physical and organizational systems that allow for the operation of society.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Ingestion (swallowing):
-
Absorbing by eating or drinking.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Inorganic:
-
Material such as sand, salt, iron, calcium salts, and other mineral materials; inorganic substances are of mineral origin, whereas organic substances are usually of animal or plant origin.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Insecticides:
-
Substances intended to repel, kill, or control insects.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Island:
-
Tract of land surrounded by water and smaller than a continent. Very small islands are included such as islets, skerries, cays, and keys.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Intervention research:
-
Scientific investigation that provides the evidence base for development and implementation of timely, effective strategies to prevent or minimize disease and disability and promote health.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
L
- Land cover:
-
The observed biophysical cover on the earth's surface, including water surfaces.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Landslide:
-
The movement of a mass of rock, earth, or debris down a slope.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Land use:
-
The total arrangements, activities, and inputs (human actions) undertaken in a certain land cover type. The term land use also describes the social and economic purposes for which land is managed (e.g., grazing, timber extraction, conservation, and city dwelling).
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Law:
-
The system of rules which a particular country or community recognizes as regulating the actions of its members and which it may enforce by the imposition of penalties.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Lead:
-
A metal with many industrial uses that is also toxic. No amount of lead is safe for people.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Leukemia:
-
A form of cancer of the blood in which the number of white blood cells is increased.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Lived experience:
-
Personal knowledge about the world gained through direct, first-hand involvement in everyday events rather than through representations constructed by other people. It may also refer to knowledge of people gained from direct face-to-face interaction rather than through a technological medium.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Liquefied natural gas:
-
Natural gas converted to liquid form by cooling to a very low temperature.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Low-emitting:
-
Gives off relatively small amounts of something.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Lupus:
-
A long-term, autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation and pain in any part of your body.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Lyme disease:
-
A bacterial infection spread by the bite of an infected tick.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
M
- Maladaptation:
-
A process that results in increased vulnerability and/or significantly undermines capacities or opportunities for present and future adaptation.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Malaria:
-
A serious disease caused by a parasite and spread by the bite of an infected mosquito; malaria is a major cause of death worldwide, but it is almost wiped out in the United States.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Malnutrition:
-
A lack of proper nutrition, including undernutrition and overnutrition that can arise from deficiencies of specific nutrients based on inappropriate combinations or proportions of foods (e.g., goiter, scurvy, anemia, and xerophthalmia caused by inadequate iodine, vitamin C, iron, and vitamin A).
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mechanistic study:
-
An experiment designed to understand a biological or behavioral process, the pathophysiology of a disease, or the mechanism of action of an intervention.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Medical visit:
-
Any utilization of the healthcare system including hospital admissions, emergency medical services, clinic, ER, or ambulance dispatch.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Melatonin:
-
A hormone that is derived from serotonin, is secreted by the pineal gland especially in response to darkness, and has been linked to the regulation of circadian rhythms.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Meningitis:
-
A viral or bacterial disease marked by inflammation of membranes in the brain and spinal cord; swimming or playing in polluted water can cause meningitis.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Mental health:
-
A state of mind characterized by emotional well-being, good behavioral adjustment, relative freedom from anxiety and disabling symptoms, and a capacity to establish constructive relationships and cope with the ordinary demands and stresses of life.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mental illness, mental disorder:
-
The conditions involving changes in emotion, thinking, or behavior (or a combination of these) and are associated with distress and problems functioning in social, work, or family activities.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mercury:
-
A silver-white poisonous heavy metallic element that is liquid at ordinary temperatures and is used especially in batteries, in dental amalgam, and in scientific instruments.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Mesoscale:
-
A measure of distance useful for local winds, thunderstorms, and tornadoes. It ranges from a few to a few hundred miles.
Source: University of California, Davis
- Mesothelioma:
-
A usually malignant tumor derived from mesothelial tissue that lines the lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs; the cancer usually starts in the lungs, but can also start in the abdomen or other organs.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Metabolite:
-
Any chemical produced as a result of a living organism’s metabolism or another substance it has absorbed.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Metastasis:
-
The process whereby a malignant cell is detached from a primary tumor and is disseminated in the body to set up secondary tumors elsewhere.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Meteorological factor:
-
Weather conditions and variables such as humidity, atmospheric pressure, or wind speed/direction.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Methylmercury:
-
Any of various toxic compounds of mercury containing the complex CH3Hg– that often occur as pollutants which accumulate in living organisms (as fish) especially in higher levels of a food chain.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Microbiome:
-
The microorganisms in a particular environment, including the body or a part of the body.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Micrometers:
-
A unit of measure; size of particulate matter particles is measured in micrometers; the average human hair is about 70 micrometers in diameter.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Mineral:
-
An inorganic substance; something neither animal nor vegetable.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Mitigation:
-
The effort to limit or reduce the severity or magnitude of something.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mixtures research:
-
The study of how environmental exposures consisting of numerous chemicals, manmade and natural, affect human health.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Model timescale:
-
A chronological measure of how distant the results are projected from the time of analysis.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Molds:
-
Microscopic organisms found indoors and outdoors that play an important role in the breakdown of plant and animal matter. When disturbed, molds release tiny cells called spores into the surrounding air.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Monsoon:
-
A seasonal change in the direction of the prevailing, or strongest, winds of a region that can cause wet and dry seasons in the area they impact.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mortality:
-
Describes the progression and severity of a given health event, and is measured as the number of deaths caused by a health event.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mountain:
-
Large natural elevation of the Earth’s surface including alpine, highlands, mountainous region.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Multidisciplinary research:
-
Scientific investigation that integrates information, data, techniques, tools, perspectives, concepts, or theories from two or more disciplines to solve problems for which solutions are beyond the scope of a single discipline.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Mutagen:
-
Anything that harmfully changes DNA in a cell, which can lead to diseases, such as cancer. Examples of mutagens include radioactive substances, ultraviolet radiation, and certain chemicals.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
N
- Naegleria:
-
A single-celled organism commonly found in warm freshwater and soil. Only one type infects people: Naegleria fowleri. Exposure symptoms range from headache and nausea to seizure and hallucination.
Source: U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Nanomaterial:
-
A material having particles or constituents of nanoscale dimensions, or one that is produced by nanotechnology.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Nanotechnology:
-
The science of manipulating materials on an atomic or molecular scale especially to build microscopic devices.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Natural experiment:
-
An observational study that exploits an event or a situation that allows for naturally random grouping of study subjects to answer a particular question.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Nature-based solutions:
-
Sustainable planning, design, environmental management, and engineering practices that weave natural features or processes into the built environment to promote adaptation and resilience. Also referred to as natural and nature based infrastructure.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Nephropathy:
-
An abnormal state of the kidney; especially: one associated with or secondary to some other pathological process.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Nervous system:
-
The organ system which consists of the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, nerve roots, autonomic nervous system, neuromuscular junction, and muscles and is involved in everyday activities such as waking up; automatic activities such as breathing; and complex processes such as thinking, reading, remembering, and feeling emotions.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Neurological disorder:
-
A disease of the central and peripheral nervous system.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Neurotransmitter:
-
A substance that facilitates the transmission of the signal from a nerve to the cell.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Neutrons:
-
An uncharged elementary particle present in all known atomic nuclei except the hydrogen nucleus.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Neutrons:
-
An uncharged elementary particle present in all known atomic nuclei except the hydrogen nucleus.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Normalized difference vegetation index:
-
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) quantifies vegetation by measuring the difference between near-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and red light (which vegetation absorbs).
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Nutritional security:
-
State when all people at all times consume food of sufficient quantity in calories and quality in terms of variety, diversity, nutrient content and safety to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life, coupled with a sanitary environment, adequate health, education and care. It differs from food security in that it also considers the aspects of adequate caring practices, health, and hygiene in addition to dietary adequacy.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
O
- Obesity:
-
A condition characterized by the excessive accumulation and storage of fat in the body.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Obesogens:
-
Artificial chemicals believed to contribute to obesity. They are found in various food containers, baby bottles, toys, plastics, cookware, and cosmetics.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Off-gas:
-
A term referring to the fact that volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in our homes are released by consumer and household products, and these chemicals then enter the indoor air we breathe.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Ore:
-
A naturally occurring mineral containing a valuable substance (such as metal) for which it is mined and worked.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Organic matter:
-
Of, relating to, or derived from living organisms.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Oxidative damage (stress):
-
Physiological stress on the body that is caused by the cumulative damage done by free radicals inadequately neutralized by antioxidants and that is held to be associated with aging.
Source: Merriam-Webster
- Ozone (O3):
-
A highly reactive gas composed of three oxygen atoms that occurs both naturally and through anthropogenic processes. Depending on where it occurs in the Earth's upper atmosphere it can have beneficial or harmful effects on the planet.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
P
- Parasite:
-
A pathogen that simultaneously injures and derives sustenance from its host.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Parkinson's disease:
-
A progressive disease of the nervous system marked by tremor, muscular rigidity, and slow, imprecise movement.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Particulate matter:
-
A mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye (PM10). Others are so small they can only be detected using an electron microscope (PM2.5).
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Patient registry:
-
An organized system that uses observational study methods to collect uniform data (clinical and other) to evaluate specified outcomes for a population defined by a particular disease, condition, or exposure, and that serves a predetermined scientific, clinical, or policy purpose(s).
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Pathogen:
-
Microorganism capable of causing disease.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS):
-
Synthetic chemicals found in many products, including food packaging, household cleaners, and nonstick cookware.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Perchlorate:
-
A molecule that can occur naturally in the atmosphere or is manufactured for industrial products such as rocket propellant, explosives, and road flares. Linked to thyroid problems in people.
Source: EPA.gov
- Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA):
-
Historically the most widespread form of PFAS in the environment. Major U.S. manufacturers no longer make it, but alternatives are used in its place.
Source: National Toxicology Program
- Permafrost:
-
A permanently frozen layer on or under Earth's surface consisting of soil, gravel, and sand, usually bound together by ice.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Pesticide:
-
A substance used for destroying insects or other organisms harmful to cultivated plants or to animals.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Petroleum:
-
An oily liquid, made of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons with small amounts of other substances, that occurs in many places in the upper strata of the earth; is prepared for use as gasoline, naphtha, or other products by various refining processes.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Pharmaceuticals:
-
Of or relating to the production and sale of drugs and medicine.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Phthalates:
-
Often called plasticizers, these chemicals make hundreds of products more durable, such as personal-care products, food packaging, toys, and flooring.
Source: Food and Drug Administration
- Phthalic anhydride:
-
A white solid with a characteristic, acrid odor. It is used in the manufacture of plasticizers; in the manufacture of unsaturated polyester resins for use in structural building parts, swimming pools, automotive parts, and luggage.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Physical injury:
-
Damage to the body occurring as a result of harm caused by accidents, falls, hits, weapons, and more.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Phytoestrogens:
-
Plant-derived compounds found in many foods such as soy. Some are linked to health benefits, including a lowered risk of osteoporosis, heart disease, and breast cancer, while others are endocrine disruptors that may harm health.
Source: EPA.gov
- Plague:
-
An infection caused by the bacterium Yersinia pesti, found mainly in rats and in the fleas that feed on them.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Planned relocation:
-
People moved or assisted to move permanently away from areas of environmental risks.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Plasticizers:
-
An additive to paint, varnish, cement or similar to increase its workability.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Pleural membrane:
-
The delicate layer of tissue that surrounds the lungs.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Pneumonia:
-
An inflammation of the tissues of the lung.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Polar:
-
Relating to the North or South poles including the arctic, sub-arctic, Antarctic, sub-Antarctic, glacier, and tundra.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Policy:
-
A course or principle of action adopted or proposed by a government, party, business, or individual.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Pollen:
-
A fine powdery substance, typically yellow, consisting of microscopic grains discharged from the male part of a flower.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs):
-
Banned in 1977 because of potential harm to immune and nervous systems, these toxic compounds remain in the environment. PCBs were used in old fluorescent fixtures, some electrical devices, and hydraulic oils.
Source: EPA.gov
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs):
-
A class of chemicals that result from burning coal, oil, gas, wood, garbage, or tobacco. They bind to or form small particles in the air. High heat when cooking meat and other foods will also form PAHs.
Source: EPA.gov
- Populations of concern:
-
A class of chemicals that result from burning coal, oil, gas, wood, garbage, or tobacco. They bind to or form small particles in the air. High heat when cooking meat and other foods will also form PAHs.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Postdoctoral fellowship:
-
A training-focused position for people who have earned a doctorate degree. It is a stepping-stone between being a student and full-time professional.
Source: Oak Ridge Institute
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD):
-
A mental health condition that develops in some people who have experienced a shocking, scary, or dangerous event.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Precipitation:
-
The amount of rain, snow, hail, or ice that has fallen at a given place within a given period, usually expressed in inches or centimeters of water.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Precision environmental health:
-
Understanding an individual's susceptibility to disease through analysis of his or her genetic profile and cumulative environmental exposures.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Predictive modeling:
-
A statistical technique to predict future events or outcomes by analyzing patterns in a given set of input data.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Prevalence:
-
The proportion of a population that has a specific characteristic in a given time period.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Promoter:
-
A region of DNA where copying a gene sequence to messenger RNA begins. The promoter region controls when and where a gene of interest will be expressed.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Psychological disorder:
-
A clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotional regulation, or behavior. Usually associated with distress or impairment in important areas of functioning.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Pubertal timing:
-
A concept indicating whether development occurs early, at the same time as, or later than the individuals' same-age, same-sex peers.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Public health:
-
The science of protecting and improving the health of populations, from neighborhoods to cities to countries to world regions, through education, promotion of healthy lifestyles, research toward prevention of disease and injury, and detecting, preventing, and responding to infectious diseases.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Public health intervention:
-
Actions taken to improve or protect the health of individuals, families, communities, and systems.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Pulmonary fibrosis:
-
The scarring or thickening of the lungs.
Source: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
- Pyrogenic:
-
A substance that causes a rise in body temperature.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
R
- Radiation:
-
The transmission of radiant energy in the forms of electromagnetic waves, streams of particles, sound or heat.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Radioactive tracers:
-
A radioactive drug used to create images of internal organs and to diagnose and treat disease; specially designed cameras allow doctors to track the path of the drug as it moves through the body.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Radioactive waste:
-
Waste exhibiting radioactivity, which is the property of emitting energetic particles (such as electrons or alpha particles) or waves resulting from the disintegration of atomic nuclei.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Radioactivity:
-
The quality of emitting or the emission of particulate or electromagnetic radiation resulting from the decay of the nuclei of unstable elements.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Radiative forcing:
-
The difference between incoming and outgoing radiation on Earth.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Radon:
-
A colorless, odorless gas. It is produced by the radioactive decay of radium. Found in small amounts in soil, rocks, and the air near the ground.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Rainforest:
-
A tropical woodland with an annual rainfall of at least 100 inches and marked by lofty broad-leaved evergreen trees forming a continuous canopy.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Rat-bite fever:
-
A rare bacterial disease spread by the bite of an infected rodent.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Reference scenario:
-
The baseline scenario used as starting point for a comparison of two or more scenarios.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Regulation:
-
The imposition of rules by government, backed by the use of penalties that are intended specifically to modify the behavior of individuals and firms in the private sector.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Remote sensing:
-
The science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically from drones, aircraft, or satellites. The process includes detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Renal system:
-
The organ system which consists of the kidney, ureters, and the urethra. The overall function of the system filters toxins from renal blood flow which allows for toxins, metabolic waste products, and excess ion to be excreted while keeping essential substances in the blood.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Reproductive system:
-
The organ system that consists of tissues, glands, and organs involved in producing children.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Research approach:
-
A plan and procedure that consists of the steps of broad assumptions to detailed methods of data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Research gap:
-
A review that identifies missing or inadequate information limiting the ability to reach a conclusion for a given research question.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Research methodology:
-
A contextual framework or rules for investigating an aspect of the study that include the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project.
Source: NIEHS EHS Glossary
- Respiratory disease:
-
A disease that affects the airways and the lungs.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Respiratory system:
-
The organs system that consists of the nose, throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs and is involved in breathing.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Reverse osmosis system:
-
A drinking water purification technology that forces water through a semipermeable membrane to remove most contaminants; also used in wastewater treatment.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Risk:
-
The chance of harmful effects to human health or to ecological systems resulting from exposure to an environmental stressor.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Risk assessment:
-
The characterization of the potential adverse effects of human exposures to hazards.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Risk management:
-
Process that evaluates options for protecting public health and the environment.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Risk perception:
-
The subjective judgment that people make about the characteristics and severity of risk.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Rocky mountain spotted fever:
-
A bacterial disease spread by the bite of an infected tick.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Rural:
-
Relating to, or characteristic of, the countryside including farmland, cropland, country, pastoral.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
S
- Salmonella:
-
A group of bacteria that is a common cause of foodborne illness.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Salmonellosis:
-
An infection with the Salmonella enterica bacteria that causes diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- SARS-CoV-2:
-
The coronavirus that is the cause of COVID-19.
Source: National Cancer Institute
- Scenario:
-
A plausible description of how the situation may develop based on a coherent and internally consistent set of assumptions about key driving forces and relationships.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Seasonality:
-
The temporal period of recurring events or processes that are correlated with particular weather patterns and daylight hours such as rising temperatures at the end of winter, the blooming of wildflowers in spring, the onset of allergies during ragweed season, and leaf-fall in autumn.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Sensitivity:
-
The ability of a cell, tissue, or organism to respond to changes in its external or internal environment. Sensitivity is a fundamental property of all living organisms.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Sentinel species:
-
Plants and animals that can biologically indicate whether certain environmental conditions may pose risks to human health.
Source: National Cancer Institute
- Septic:
-
Used for sewage treatment and disposal.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Serious mental illness (SMI):
-
In the context of scientific research, generally refers to people with diagnoses of schizophrenia, major depression, and bipolar disorder regardless of functioning at any given point in time.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Silica dust:
-
A natural compound of silicon and oxygen found mostly in sand.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Silicosis:
-
A lung disease caused by breathing in (inhaling) silica dust.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Sinusitis:
-
An inflammation of the sinus.
Source: Illustrated Dictionary and Resource Directory of Environmental and Occupational Health
- Smelter:
-
A facility that melts or fuses ore to separate its metal content; emissions may cause pollution.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Smog:
-
The brownish haze that pollutes the air, making it difficult for some people to breathe; its primary component is ozone.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Social determinants of health (SDOH):
-
The conditions in the environments where people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning, and quality-of-life outcomes and risks.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Social stratification:
-
The differentiation of a specified population into defined socioeconomic categorizations based on factors such as wealth, income, race, education, and power.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Social vulnerability index:
-
The resilience of communities when confronted by external stresses on human health, stresses such as natural or human-caused disasters, or disease outbreaks.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Sociodemographic vulnerability:
-
An individual or community's potential for harm resulting from the comination of Social Determinants of Health such as income, education, race/ethnicity, as well as factors such as resilience and adaptive capacity.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Socioeconomic status (SES):
-
The social standing or class of an individual or group. It is often measured as a combination of education, income, and occupation.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Solar radiation:
-
The electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Sterilize:
-
To kill germs to prevent infections.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Storm surge:
-
The abnormal rise in seawater level during a storm, measured as the height of the water above the normal predicted astronomical tide.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Styrene:
-
An unsaturated liquid hydrocarbon obtained as a petroleum byproduct, used to make plastics and resins.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Subsistence fishing/hunting:
-
A system of hunting or fishing that provides all or almost all the goods required by the family, usually without any significant surplus for sale.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Substance use disorders:
-
A medical illness caused by repeated misuse of a substance or substances. Note: Severe substance use disorders are commonly called addictions.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Suburban:
-
Residential communities outside central urban areas. Primarily characterized by sprawling, low-density development; single-family residential uses; automobile dependence; and long-distance commutes into the central city for work.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Suicide:
-
Death caused by injuring oneself with the intent to die.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Sulfur dioxide:
-
A colorless, water-soluble, acidic gas that is produced from the combustion of fossil fuels.
Source: Dictionary of Environmental Health
- Surveillance:
-
The ongoing interpretation of data, closely integrated with the timely dissemination of these data to those responsible for preventing and controlling disease and injury.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Surveillance system:
-
A program which includes the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data essential to planning, implementation, and evaluation of a practice.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Synthetic:
-
Of, relating to, or produced by chemical or biochemical synthesis; especially: produced artificially.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
T
- Tailings:
-
Residue separated in the preparation of various products (such as grain or ores)—usually used in plural.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Tallow:
-
The white, nearly tasteless solid-rendered fat of cattle and sheep used chiefly in soap, candles, and lubricants.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Textiles:
-
Woven or knit fabric; a fiber or yarn used in making cloth.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Thermoregulation:
-
The process of maintaining the core internal temperature of the body.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Thyroid gland:
-
An organ located beneath the larynx (voice box) that makes hormones that regulate growth, development and metabolism.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Tidal flats:
-
Commonly muddy or marshy land that is covered and uncovered by the rise and fall of tides.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Titanium dioxide:
-
A powder used as a white pigment in products such as sunscreens, cosmetics, paints, and plastics. Repeated exposure may cause bronchitis with coughing, phlegm, or shortness of breath.
Source: New Jersey Department of Health
- Toxicogenomics:
-
Study of the roles that genes play in the biological responses to environmental toxicants and stressors by the collection, interpretation, and storage of information about gene and protein activity.
Source: Environmental Protection Agency
- Toxicology:
-
The branch of science concerned with the nature, effects, and detection of poisons.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Toxin:
-
Biological agents that can cause harmful effects on people.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Training:
-
Lessons and learning opportunities that develop skills and knowledge related to useful competencies.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Transdisciplinary research:
-
A scientific investigation conducted by investigators from different disciplines working jointly to integrate new conceptual, theoretical, methodological, and translational approaches to address a common problem.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Translational research:
-
Turns scientific discoveries made in a laboratory, clinic, or fieldwork into new medical treatments and health approaches that improve well-being.
Source: N/A
- TRAP:
-
Air pollution that comes from fossil fuel combustion in motor vehicles.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Trauma:
-
Results from an event or events that are experienced by an individual as physically or emotionally harmful or life threatening and that have lasting adverse effects on the individual’s functioning and mental, physical, social, emotional, or spiritual well-being.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Trauma-informed care (TIC):
-
Refers to either evidence-based trauma interventions or to a broader systems-level approach that integrates trauma-informed practices throughout a service delivery system.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Treaty:
-
An international agreement governed by international law, whether embodied in a single instrument or in two or more related instruments and whatever its particular designation. The term as a matter of U.S. constitutional law denotes international agreements made by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate in accordance with Article II, section 2 of the Constitution of the United States.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Tundra:
-
A treeless, level, or gently undulating plain characterized by low temperatures, little precipitation, poor nutrients, and short growing seasons. There are two types: arctic and alpine.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
U
- Un-ventilated:
-
The circulation of air through a building in order to expel noxious air and admit clean, fresh air.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Urban:
-
Relating to, characteristic of, or constituting a city.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Urban heat island effect:
-
The tendency for higher air temperatures to persist in urban areas as a result of heat absorbed and emitted or reflected by buildings, asphalt and other impervious surfaces, which tend to make these areas warmer than the surrounding countryside.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
V
- Valley:
-
A low area of land between hills or mountains, typically with a river or stream flowing through it.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Vape:
-
The action or practice of inhaling and exhaling the vapor produced by an electronic cigarette or similar device.
Source: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Vector:
-
An organism, frequently an arthropod such as a mosquito or tick, which transmits a pathogen from one host to another.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Vector-borne disease:
-
A disease or illness caused by parasites, viruses, and bacteria that are transmitted by vectors.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Ventilation:
-
The circulation of air through a building in order to expel noxious air and admit clean, fresh air.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Vertigo:
-
A feeling of dizziness or lightheadedness, or that the room is spinning.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Virus:
-
An infective agent that can cause disease by infecting a cell, making copies of itself, and multiplying.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Vitamin D:
-
Vitamin D is a nutrient you need for good health. It helps your body absorb calcium, one of the main building blocks for strong bones. Together with calcium, vitamin D helps protect you from developing osteoporosis, a disease that thins and weakens the bones and makes them more likely to break. Your body needs vitamin D for other functions too. Your muscles need it to move, and your nerves need it to carry messages between your brain and your body. Your immune system needs vitamin D to fight off invading bacteria and viruses.
Source: National Institutes of Health
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs):
-
Many VOCs are human-made chemicals used to manufacture paints, dry cleaning agents, and refrigerants. Emitted as gases, they can affect indoor air quality.
Source: EPA.gov
- Vulnerability:
-
The tendency or predisposition to be adversely affected by stressors or impacts of health effects. Vulnerability is a function of adaptive capacity and sensitivity.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Vulnerability assessment:
-
An evaluation process used to identify the populations or communities who are the most vulnerable or are at highest risk of a given exposure or event. In contrast, risk assessments are used to characterize risks for other purposes, such as policy analysis.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
W
- Water quality:
-
A measure of the suitability of water for a particular use based on selected physical, chemical, and biological characteristics.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Water-borne illness:
-
A disease or illness caused by a variety of microorganisms, biotoxins, and toxic contaminants, which leads to adverse health impacts.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Watershed:
-
A land area that channels rainfall and snowmelt to creeks, streams, and rivers, and eventually to outflow points such as reservoirs, bays, and the ocean.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Well-being:
-
A state of existence that fulfills various human or community needs, including material living conditions and quality of life, as well as the ability to pursue one’s goals, to thrive, and feel satisfied.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- West nile virus:
-
An infectious disease spread by the bite of an infected mosquito that can cause illness or death and is a zoonotic disease for which wild birds are the primary reservoir host.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Wet bulb globe temperature:
-
Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) is a measure of the heat stress in direct sunlight, which takes into account: temperature, humidity, wind speed, sun angle and cloud cover (solar radiation). This differs from the heat index, which takes into consideration temperature and humidity and is calculated for shady areas.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Wetland:
-
An area where water covers the soil, or is present either at or near the surface of the soil, all year or for varying periods during the year, including during the growing season including a marshland and swampland.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
- Wildfire:
-
An unplanned fire that burns in a natural area such as a forest, grassland, or prairie.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary
Y
- Yellow fever:
-
A viral infection spread by mosquitoes.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
Z
- Zika virus:
-
A virus that is spread mostly by mosquitoes; a pregnant mother can pass it to her baby during pregnancy or around the time of birth; it can spread through sexual contact.
Source: U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Zoonotic disease:
-
A disease that is transmitted from an animal or nonhuman species to humans.
Source: NIEHS EHS glossary