Community Partnership’s Soil Sampling Workshops Address Lead Exposure Risk
Through a community gardening partnership, Emory University researchers tested soil and found high lead levels. In response, they implemented a neighborhood soil sampling workshop and have continued working with urban gardeners on safety initiatives. The project began in 2016.
The Saikawa lab, which is associated with Emory’s HERCULES Exposome Research Center and the Historic Westside Gardens, an Atlanta-based gardening organization, started the soil testing effort in west Atlanta. A March 2023 paper and a July 2023 paper describe the research team’s work in community-engaged soil screening initiatives and their continuation. Listen to the April 2022 PEPH podcast to hear more about the soil sampling study.
Initiating the Soil Sampling Project
When the City of Atlanta planned to develop urban gardens, the Saikawa lab wanted to see if the soil in the lots was safe. The urban agriculture project was proposed as a way to address food insecurity and increase access to healthy food.
Researchers from the Saikawa lab found soil lead levels exceeded the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) threshold. As a result, the Saikawa lab and the Historic Westside Gardens partnered to expand screening efforts and community engagement around soil safety for gardening. When the soil was sampled and tested, the partners found that three of 11 home gardens in the neighborhood had unsafe lead levels.
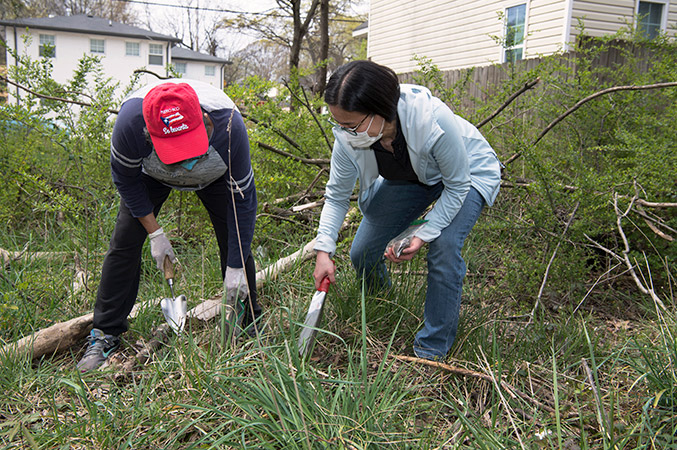

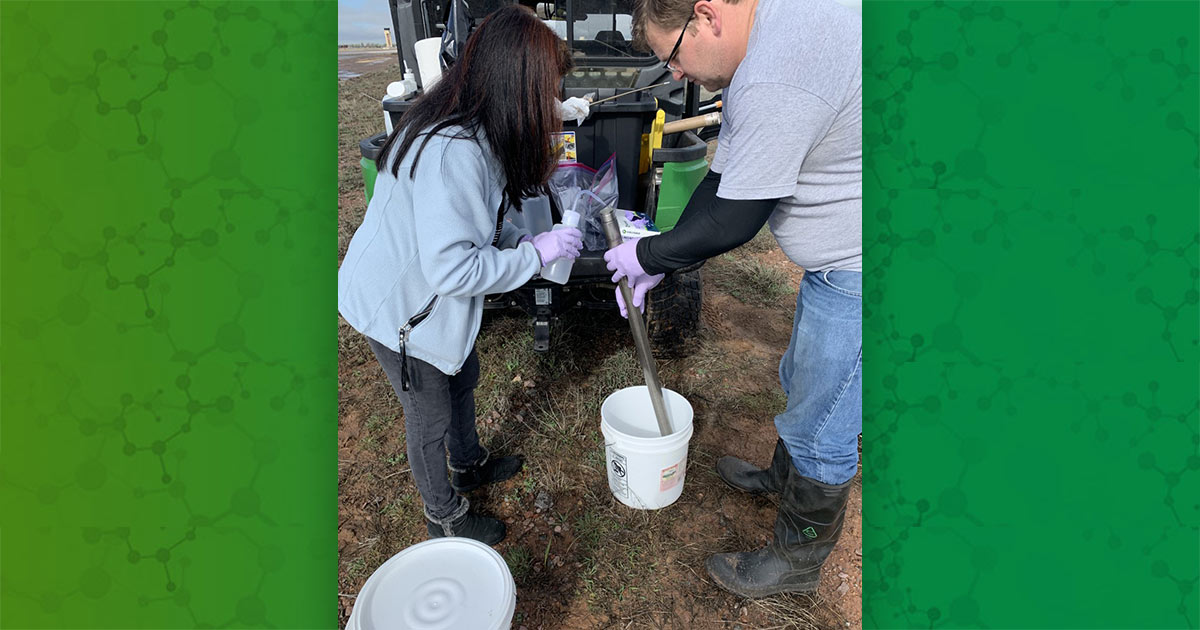
Eri Saikawa and Rosario Hernandez, executive director of Historic Westside Gardens, collect soil samples from a yard. (Photo courtesy of Emory University)
In August 2018, the Saikawa lab and Historic Westside Gardens collected more soil samples from the community by hosting a Soil Screening, Health, Outreach, and Partnerships (soilSHOP) event during a local tomato festival. At this event, a resident brought a soil sample containing a rock-like substance that she was concerned about. Staff from the EPA identified the substance as slag, an industrial waste product of ore smelting. Researchers from the Saikawa lab analyzed the sample and found high lead levels. The research team shared the results with the state government who referred the issue to appropriate authorities at the EPA.
“This discovery made us go around in the neighborhood to look for slag,” stated Eri Saikawa, Ph.D., professor at Emory University’s Department of Environmental Sciences, and member of HERCULES. “We found many slag pieces visibly present in Atlanta’s Westside neighborhoods, and we realized the lead contamination may be present at a large scale.”

Saikawa and Hernandez walk through a neighborhood in west Atlanta. (Photo courtesy of Emory University)
The slag finding triggered several efforts. The EPA began investigating soil in nearly 60 lots in west Atlanta where the slag was initially found. They found high soil lead levels in more than half of the lots. As more testing was conducted, more lead contamination was found, and over time the area expanded to 2,097 lots. The area is now designated as a Superfund site and has been listed on the National Priorities List since March 2022.
At the same time, the team worked with the EPA to gain the community’s trust and participated in raising awareness by conducting door-to-door outreach. They also began providing seeds for plants that take up lead to help the community reduce soil lead levels. The team also hosted more soilSHOPs in majority-Black neighborhoods that faced socioeconomic disadvantages to screen for lead and address community-level environmental health issues. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the team established a virtual soilSHOP for residents throughout Georgia so more people could learn how to test their soil samples without in-person events.
Lead in soil is a public health concern because children who play outdoors and people who garden or participate in urban agriculture may be at greater risk of lead exposure. In fact, in the Federal Action Plan to Reduce Childhood Lead Exposure and Associated Health Impacts, the President’s Task Force on Environmental Health Risks and Safety Risks to Children cites reduction of lead in soil as a way to reduce childhood lead exposure.
Engaging the Community in Soil Sampling
The soil sampling project was initially planned as a small project for a graduate student. However, when high soil lead levels were found, the team sought help from the HERCULES research center. Through the HERCULES Stakeholder Advisory Board, a new partnership developed between the Saikawa lab, Historic Westside Gardens, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, and the EPA on soil lead contamination.
The soilSHOPs provided residents the opportunity to bring soil samples for free lead testing. To prepare for the events, partners sent out educational materials to residents with information on how to collect soil and get it tested. The partners were also at the events to present information on lead safety and the health risks of exposure. During COVID, drop-off boxes were set up and participants received information along with their soil test results via email.
Now, the Saikawa lab has increased its relationship with various community organizations and is hosting more soilSHOPs at local community events and at local middle and high schools.
“The partnership with the Historic Westside Gardens was a way for us to engage with residents, especially those who were interested in gardening and could therefore be exposed to soil lead,” reflected Saikawa. “Historic Westside Gardens was instrumental in getting residents involved in soil testing in the west Atlanta neighborhood and now we try to implement it in wider areas.”
Health Concerns at the Superfund Site
The Saikawa lab and the partners are now focused on addressing concerns raised by the community since the Superfund designation. For example, residents have expressed concerns about the lack of health assessments for the residents despite the Superfund designation. Those whose soil tested just below the EPA soil lead standard fear that their families, especially children, may still be at risk of negative health effects. Some have inquired about using plants as a cleanup method since it is a cost-effective way to reduce soil lead and beautify the neighborhood. The researchers and community partners continue working with the community to spread awareness of soil lead contamination and its health consequences and to assess children’s cumulative lead exposures.
As one resident stated, “This goes beyond just cleaning up the soil. This is about our health, and the health of our grandchildren growing up here now.”
Environmental Protection Agency Seeks Public Comment on Public Participation in Its Decision-Making
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released a draft policy, Achieving Health and Environmental Protection Through EPA’s Meaningful Involvement Policy, in mid-November and is seeking public comment on it. The policy describes how the EPA will engage with the public and provide public involvement in all its programs. EPA recognizes that its activities related to health and environmental protections are stronger when they are informed by people with lived experience. The draft policy is an update to EPA’s 2003 Public Involvement Policy, which was itself an update from its 1981 Public Participation Policy. The new draft describes three steps for meaningful involvement:
- Identifying decision(s) in an EPA action that may be influenced by public input.
- Using the public participation model.
- Using the public participation spectrum.
Comments are due January 16, 2024.
NIH Updates Fact Sheet on Reducing Health Risks From Warming Temperatures and Weather Disasters
NIH’s Climate Change and Health Initiative updated its fact sheet detailing the initiative’s major accomplishments on Reducing Health Risks from Warming Temperatures and Weather Disasters. The October update reflects progress the initiative has made since starting in 2022. The Climate Change and Health Initiative is a cross-cutting NIH effort that was created to address health threats from climate change and build resilience in communities. In terms of research funding updates, the initiative established a coordinating center to convene, accelerate, foster, and expand the community of practice on climate and health and awarded 19 administrative supplements to expand the climate and health research capacity of existing grants. The initiative also formed a new partnership with the National Science Foundation to support rapid funding to researchers addressing climate-related disasters, supported pilot projects focused on basic and applied research on the health effects of climate change, and created a Climate and Health Scholars program. The program’s inaugural class of scholars helped build capacity for conducting climate-related and health research, and a second cohort is participating in 2023-2024.
NIH Encourages Citizen Science
NIH is encouraging people to be citizen scientists to help medical research, as described in the November NIH News in Health newsletter. It explains citizen science and details various NIH projects for which citizen scientists can contribute. For example, the All of Us project aims to enroll at least one million people nationwide to help researchers understand how different factors, such as genetics and cultural practices, can affect human health.
Some activities are online games. The MindCrowd project, in which volunteers take a 10-minute memory test, is focused on elucidating how brain function changes with age, and the Eyewire project asks volunteer players to interact with images of brain tissue to help map the human brain.
“One clear message we get from community members is that they don’t just want to be the subjects of research. They want to be active partners,” says NIH’s Liam O’Fallon, an expert in community-engaged science and the PEPH Coordinator. “They want to help with defining the questions and collecting the data. And they want to help communicate the findings.”

PEPH Environmental Health Chat Podcast Series
PFAS in Drinking Water: Responding to Community Concerns
PEPH Environmental Health Chat Podcast Series
PFAS in Drinking Water: Responding to Community Concerns
Residents in several North Carolina communities had questions about their exposure and health effects after PFAS were found in their drinking water. To help answer their questions, NIEHS-funded scientists started the GenX Exposure Study. In this episode, Jane Hoppin, Sc.D., lead scientist of the study, describes findings and strategies the team uses to engage communities and share results.

PEPH Grantee Highlight
Kathleen Vandiver, Ph.D.
Kathleen Vandiver, Ph.D., Director of the Center for Environmental Health Sciences and the Superfund Research Program at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), is passionate about engaging the public on environmental health issues. She joined MIT in 2005 as a community engagement and education specialist and continues to focus on developing accessible tools and resources to teach environmental health concepts to communities affected by environmental contamination. Vandiver and team found that a river affected by industrial contamination was safe for recreational boat users despite the presence of a toxic chemical. The results supported efforts for the community to develop the river area into a park. Through her work with MIT’s Superfund Research Program, Vandiver has worked with communities to develop interactive online modules addressing questions about chemical exposures and has partnered with the Passamaquoddy Tribe in Maine to address environmental health concerns.
Funding Opportunities
PHS 2023-2 Omnibus Solicitation of the NIH and CDC for Small Business Innovation Research Grant Applications (Parent SBIR [R43/R44] Clinical Trial Required)
Invites eligible United States small business concerns to submit Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase I, Phase II, Direct to Phase II (NIH only), Fast-Track (NIH only), and Phase IIB (NIH only) grant applications. The PHS 2023-2 SBIR/STTR Program Descriptions and Research Topics for NIH, CDC, and FDA represent scientific program areas that may be of interest to applicant small businesses in the development of projects that have potential for commercialization. Small business concerns that have the research capabilities and technological expertise to contribute to the research and development mission(s) of the NIH and CDC awarding components identified in this funding opportunity are encouraged to submit SBIR grant applications in these areas. A related SBIR funding opportunity is available without a clinical trial requirement: PHS 2023-2 Omnibus Solicitation of the NIH, CDC and FDA for Small Business Innovation Research Grant Applications (Parent SBIR [R43/R44] Clinical Trial Not Allowed). Related funding opportunities are available for small business applicants interested in submitting small business technology transfer (STTR) applications: PHS 2023-2 Omnibus Solicitation of the NIH for Small Business Technology Transfer Grant Applications (Parent STTR [R41/R42] Clinical Trial Not Allowed) and PHS 2023-2 Omnibus Solicitation of the NIH for Small Business Technology Transfer Grant Applications (Parent STTR [R41/R42] Clinical Trial Not Allowed).
Deadlines: January 5, 2024; April 5, 2024
SBIR/STTR Commercialization Readiness Pilot (CRP) Program Technical Assistance and Late-Stage Development (SB1, Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Encourages applications from small business concerns to the newly re-authorized Commercialization Readiness Pilot (CRP) program. The funding opportunity aims to facilitate the transition of previously or currently funded Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) Phase II and Phase IIB projects to the commercialization stage by providing additional support for technical assistance and later stage research and development not typically supported through Phase II or Phase IIB grants or contracts. This may include independent replication of key studies, Investigational New Drug-enabling studies, clinical studies, manufacturing costs, regulatory assistance, or a combination of services. Although a significant amount of the work in a CRP award may be subcontracted to other institutions, the small business concern is expected to maintain oversight and management of research and development throughout the award.
Deadlines: January 5, 2024; April 5, 2024
HHS Environmental Justice Community Innovator Challenge
. The Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health and the Office of Minority Health are seeking community-led strategies and tools to address health disparities in communities disproportionately impacted by environmental risks and hazards including those related to climate change, and the cumulative impacts of other stressors. This Challenge seeks to support to community-based and Tribal organizations in areas including, but not limited to: development or implementation community-driven strategies to address health disparities; effective partnerships between community-based or Tribal organizations and other civil organizations, such as faith-based, health care and public health and educational organizations, to address environmental and climate change-related hazards and support community resilience; and innovative approaches to building capacity in community-based or Tribal organizations on project planning, needs assessment, budgeting, engagement with community members, and grant application writing, to address environmental and climate change-related hazards as drivers of health disparities. The competition has two phases. All eligible submissions will be evaluated, and separate prizes will be awarded for each of the two phases. The first phase is currently open for submissions.
Deadline: January 30, 2024
Notice of Special Interest (NOSI): Research on the Health of Women of Understudied, Underrepresented, and Underreported (U3) Populations (Admin Supp Clinical Trial Optional)
Supports projects investigating inequities in women’s and girls’ health and intervention studies to improve equity. Projects that emphasize and integrate measures beyond the individual level and consider perspectives from multiple disciplines are of specific interest. A broad range of research topics studied at the preclinical, clinical, behavioral, and translational levels — including proposals incorporating multilevel interventions, using community-engaged approaches, and focusing on one or more NIH-designated health disparities populations — are encouraged.
Deadline: January 31, 2024
Research Supplements to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research (Admin Supp — Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports administrative supplements to recruit and support high school, undergraduate and graduate/clinical students, postbaccalaureate and post-master’s individuals, postdoctoral researchers (including health professionals), and eligible investigators. NIH encourages institutions to diversify their student, postdoctoral researchers, and faculty populations to enhance the participation of individuals from groups that are underrepresented in the biomedical, clinical, behavioral, and social sciences, such as individuals from racial and ethnic groups that have been underrepresented in the sciences; individuals with disabilities; individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds; and women from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Deadline: February 1, 2024
Research With Activities Related to Diversity (ReWARD) (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
ReWARD funding will support research in areas related to the programmatic interests of NIEHS and ongoing diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility activities focused on enhancing diversity in the biomedical research enterprise within the U.S. and territories. This funding is intended for individuals with no current NIH research project grant funding at the time of the award. This announcement requires a Plan for Enhancing Diverse Perspectives as part of the application.
Deadline: February 5, 2024
Notice of Special Interest (NOSI): Data Informed, Place-Based Community-Engaged Research to Advance Health Equity
This NOSI is meant to stimulate community-engaged research that leverages geospatial data to probe the influence of geographic factors on disease development and health outcomes. Its goal is to use place-based research to help advance health equity in different communities. Applicants must select the IC and associated NOFO to use for submission of an application in response to the NOSI. NIEHS is interested in applications that integrate place-based environmental data with other data types and sources (such as human behavior and time-activity patterns, environmental data collected by low-cost sensor networks or wearable technologies, biomonitoring data, and other molecular or clinical outcome data) to improve exposure estimates at both the community and individual level, to advance understanding of the effects of environmental exposures on health outcomes, and to inform prevention and intervention strategies. Applicants may apply through PA-20-185 or PA-20-195.
Deadlines: February 5, 2024; June 5, 2024; October 5, 2024
Undergraduate Research Education Program (UP) to Enhance Diversity in the Environmental Health Sciences (R25 Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports educational activities that encourage individuals from diverse backgrounds, including those from groups underrepresented in the biomedical and behavioral sciences, to pursue further studies or careers in research. NIEHS UP (R25) programs supported by this NOFO are expected to consist of both an introduction to environmental health sciences research through experience on a research project with the participating faculty and an organized educational program (seminars, etc.) designed to acquaint participants with the larger field of environmental health sciences. The focus of both the research experience and the educational experiences should be within the mission interests of NIEHS, which explores how the environment affects people’s health. Programs which propose only the research experience within the context of a university-wide program for undergraduate students will not be considered responsive to this announcement.
Deadline: February 14, 2024
Notice of Special Interest: Administrative Supplements to Recognize Excellence in Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Accessibility Mentorship
Supports administrative supplements to existing NIH awards to support scientists who have demonstrated compelling commitments and contributions to mentorship and enhancing diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility (DEIA) in the biomedical sciences. This Notice of Special Interest (NOSI) encourages program directors and principal investigators to promote DEIA and mentorship broadly and as such differs from a Diversity Supplement (PA-23-189). Diversity supplements are designed to support research experiences for individuals from diverse backgrounds, including those from underrepresented groups, through the career continuum from high school to the faculty level. In contrast, this NOSI focuses on mentors who have dedicated their time and effort and have made significant contributions, based on evaluation data and publications, to DEIA. Mentors are encouraged to apply for an administrative supplement to further their personal research and/or mentoring activities.
Deadline: February 16, 2024
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Predoctoral Fellowship (Parent F31)
The Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Individual Predoctoral Fellowship (Parent F31) award enables promising predoctoral students to obtain individualized, mentored research training from outstanding faculty sponsors while conducting dissertation research in scientific health-related fields relevant to the missions of participating NIH Institutes and Centers. The proposed mentored research training must reflect the candidate’s dissertation research project and is expected to clearly enhance the individual’s potential to develop into a productive, independent research scientist. Funding opportunities are also open for the Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Individual Fellowship for Students at Institutions with NIH-Funded Institutional Predoctoral Dual-Degree Training Programs (Parent F30), which supports promising predoctoral students who are matriculated in a combined M.D./Ph.D. or other dual-doctoral degree training program, and who intend careers as physician/clinician-scientists; the Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Individual Senior Fellowship (Parent F33), which supports experienced scientists who wish to make major changes in the direction of their research careers or who wish to broaden their scientific background; the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Fellowship for Students at Institutions Without NIH-Funded Institutional Predoctoral Dual-Degree Training Programs (Parent F30) to enhance the integrated research and clinical training of promising predoctoral students, who are matriculated in a combined M.D./Ph.D. or other dual-doctoral degree training program, and who intend careers as physician/clinician-scientists; the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Postdoctoral Fellowship (Parent F32) to support research training of highly promising postdoctoral candidates who have the potential to become productive, independent investigators; and the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Predoctoral Fellowship to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research (F31-Diversity) to enhance the diversity of the health-related research workforce by supporting the research training of predoctoral students from diverse backgrounds.
Deadline: April 8, 2024
Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
Supports research on interventions to improve health in Native American populations. This includes 1) etiologic research that will directly inform intervention development or adaptations, 2) research that develops, adapts, or tests interventions for health promotion, prevention, treatment, or recovery, and 3) where a sufficient body of knowledge on intervention efficacy exists, research on dissemination and implementation that develops and tests strategies to overcome barriers to the adoption, integration, scale-up, and sustainability of effective interventions. The inclusion of Native American investigators serving on the study team or as the program director or principal investigator is strongly encouraged. This funding opportunity is part of the Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health initiative, which also includes Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health (R21 Clinical Trials Optional), and Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health (R34 Clinical Trial Optional). For the R01 and R21 funding mechanisms, NIEHS is interested in applications that focus on the development, adaptation, efficacy, effectiveness, implementation, or sustainability of culturally appropriate interventions to prevent or mitigate the health impacts of environmental exposures that disproportionately impact Native American populations. For the R34 funding mechanism, NIEHS is interested in applications that support the initial development of a culturally appropriate clinical trial or research project in preparation for health promotion or disease prevention interventions addressing the health impacts of environmental exposures that impact Native American populations.
Deadline: October 1, 2024
Environmental and Climate Justice Community Change Grants Program
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is accepting applications for its Environmental and Climate Justice Community Change Grants program. The program provides Inflation Reduction Act funds in environmental and climate justice activities to benefit disadvantaged communities through projects that reduce pollution, increase community climate resilience, and build community capacity to address environmental and climate justice challenges. These place-based investments will be focused on community-driven initiatives to be responsive to community and stakeholder input. The entities eligible to apply under this opportunity are:
- A partnership between two community-based non-profit organizations.
- A partnership between a community-based non-profit organization and one of the following:
- A Federally-Recognized Tribe.
- A local government.
- An institution of higher education.
Other organizations and entities may be able to participate and be involved in the Community Change Grants projects as collaborating subrecipients and/or procurement contractors selected in compliance with competition requirements. The EPA is accepting applications on a rolling basis; therefore, interested applicants are encouraged to apply early. To apply for this opportunity, see the announcement on Grants.gov.
Deadline: November 21, 2024
Upcoming PEPH-related Events
PEPH: Meet the Editors (webinar). The chief editors of three journals will speak about their journals’ visions, general focus, and new topics of interest. The three journals are Environmental Health Perspectives, the Journal of Health and Pollution, and the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology. Registration is available.
National Environmental Health Association’s Environmental Health Grand Rounds: Radon and Uranium in Groundwater (webinar). The speaker will talk about the environmental public health impacts of radon and uranium in groundwater in Wake County, North Carolina, where one in 10 private wells is contaminated. After the presentation, a panel of groundwater and well experts will discuss the roles and responsibilities of the environmental public health workforce. This webinar is part of the Environmental Health Grand Rounds series, which is geared toward undergraduate and graduate students in environmental sciences and public health. Registration is available.
USA Exposome Symposium: Children’s Health, Environmental Justice and the Exposome (Nashville, Tennessee). The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Institute for Exposomic Research and Meharry Medical College are hosting a symposium on the intersection of the exposome, children’s health, and environmental justice. The symposium will bring together academic, government, and community partners to share research findings; discuss the use of computational analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning in analyzing large data sets; and discuss translational interventions and policies to reduce the effects of environmental injustice on children’s health. Registration is available.
International Society of Exposure Science Panel Discussion Webinar: Exposure Science in Latin America (online). Researchers who work in Latin America will present insights on their community engagement and exposure science work in low-income communities in low- and middle-income countries. Registration is available.
International Society of Exposure Science: Public Sector Panel Discussion. The mentorship committee of the International Society of Exposure Science will host this panel discussion focused on public sector careers within the field of exposure science. The discussion will be geared toward people who are interested in careers in exposure science, either as a career change or a new career as they prepare to graduate. Society members and non-members are welcome to attend. Registration is available.
PEPH Meeting: Climate Change and Environmental Justice – Engaging Diverse Teams (Durham, North Carolina). PEPH grantees and partners are invited to attend this meeting to discuss common issues, approaches, and opportunities in climate change and environmental justice. There will be poster sessions and workshops in which participants will share skills, trainings, and approaches. Learn more on the meeting webpage.