Report-Back on Wearable Monitors Increases Air Pollution Awareness
Researchers from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and the University of Kentucky who worked on the NIEHS-funded Ecological Momentary Assessment and Personal Particle Exposure (EcoMAPPE) study, which measured adolescents’ personal exposure to air pollution through wearable monitors, wanted to ensure study participants received effective and actionable reports on their exposure. They did this by engaging with participants and their caregivers to design report-back materials. The design process is described in a March 2023 paper.
The researchers also surveyed participants and their caregivers about the perceived benefits of the report-back materials. After receiving the materials, participants and their caregivers reported increased knowledge, attitudes, and awareness about air pollution. A November 2023 paper describes the survey process and results.
“Most prior studies of report-back materials have focused on chemical or other biomonitoring data. Our study is perhaps the first to look at participant perceptions on benefits of wearable air pollution monitoring report-back materials,” stated Patrick Ryan, Ph.D. “Effectively co-designing report-back materials with study participants to ensure the information is communicated in an understandable and usable way can benefit participants in knowing where and when their exposure to air pollution occurs. We also saw evidence that it increased participants’ knowledge and awareness of air pollution in general.”

Students walk together outdoors. School-age participants in the EcoMAPPE study wore air monitoring devices to measure air pollution throughout the day. (Photo courtesy of George Pak of Pexels)
Engaging Study Participants and Parents to Design Report-Back Materials
Wearable air monitors can provide actionable information to community residents because they directly measure where and when a wearer was exposed to air pollution. It is important to report these results back to users in a timely, effective, and easily understandable way so they can act on their personal results. With this in mind, EcoMAPPE researchers hosted focus groups in which participants, ages 13 – 17, who had previously worn personal air monitors provided feedback on the design of report-back materials. Researchers also engaged participants’ caregivers in a separate focus group.
Eight EcoMAPPE participants and their caregivers provided feedback in the focus groups. In both the adolescent and caregiver focus groups, participants described the EcoMAPPE study in their own words so researchers could learn how a lay audience would understand the study. These words and phrases were later incorporated into the language used in the report-back materials. Participants also reviewed and gave feedback on prototypes of report-back materials developed by the researchers. Prototypes were in an electronic format and included sample graphs of results and information about air pollution.
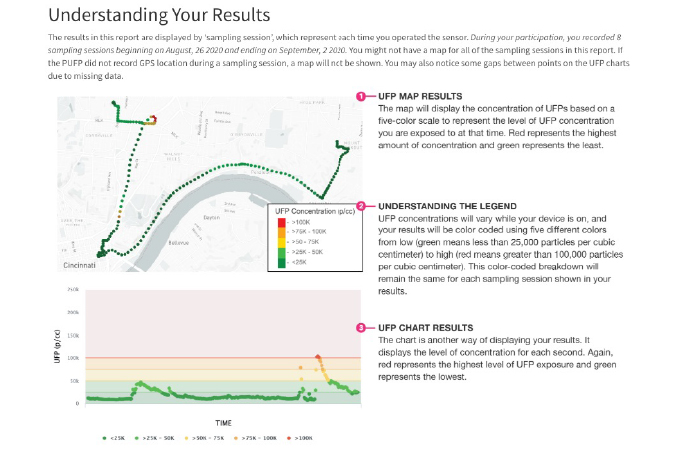
A screen shot of part of the report-back materials showing a prototype of air pollution measurement graphs and explanations for users. (Photo courtesy of Pat Ryan)
The adolescent focus group members helped develop the prototypes by selecting components they liked best. A prominent portion of the reports included maps showing where wearable devices recorded participants’ locations and corresponding air pollution exposure levels. To show how they would want the map to look, each focus group participant also drew a sample map that displayed air pollution results. They also added an explanation of the results in their own words. Participants then reviewed all prototypes and drawings and selected which components they liked best.
Researchers made draft report-back documents based on both groups’ feedback, including input on the materials’ presentation, content, readability, and usability. The final report-back document included:
- A comparison of participants’ median exposure compared to the entire study population.
- A guide to understanding the personal air monitor and results.
- A visualization of personal measurement data using an interactive map with data on days and times of exposures.
- An introduction to the materials, including an overview of air pollutants.
- Information on sources of air pollutants, potential health risks, and strategies to reduce exposure.
“Engaging with the focus groups members was a critical step to help us design effective report-back materials,” reflected Ryan. “Doing so made sure the reports captured results in a way that was meaningful to the participants.”
Surveying Study Participants on Changes in Knowledge, Attitudes, and Awareness
All EcoMAPPE participants were invited to receive the report-back materials and participate in surveys to assess their knowledge, attitudes, and awareness of air pollution before and after receiving the materials. Of the original 118 adolescent EcoMAPPE participants, 37 completed the surveys. Additionally, 68 caregivers completed the surveys.
The survey results revealed positive increases in study participants’ and caregivers’ awareness of air pollution, and greater confidence among study participants in their ability to reduce their exposure to air pollutants. Study participants expressed excitement about using air monitors and contributing to science. The survey results also showed increased knowledge about air pollutants among caregivers but not among study participants.
“Findings showed that well-designed, co-developed, culturally appropriate report-back materials may increase study participants’ awareness of how, when, and where they are exposed to high air pollution levels,” stated Ryan. “From this research, we think personal report-back materials could be a potential intervention to reduce exposure to air pollution but would need to examine this further.”
New Centers of Excellence Support Community Heat Monitoring and Resilience
In May, the Department of Commerce and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration announced funding for two centers of excellence that will support community heat monitoring and resilience. The funding will allow the National Integrated Heat Health Information System, a federal interagency group, to better support community data collection on extreme heat and help communities as they plan and evaluate equitable heat resilience projects. The center, based in Durham, North Carolina, will support community-serving organizations as they conduct local climate and health studies. The second center, based in Los Angeles, will support decision-making related to heat risk reduction. The centers build on eight years of federal efforts to map urban heat islands in support of cities’ decision-making around heat risk.
New Resource Provides Access to Datasets from Satellites to Further Environmental Justice Efforts
In April, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) published its Environmental Justice Data Search Interface, a resource that provides streamlined access to environmental justice data from Earth observation satellites. Search results from the interface include not only relevant datasets, but also customizable information about each dataset, such as its strengths, limitations, spatial coverage, and temporal coverage. The resource allows both general searches and searches within eight focus areas such as climate change, extreme heat, and urban flooding. A tutorial is available through the interface’s homepage, and a video overview is also available.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Publishes Reports to Help Standardize Use of Low-Cost Air Sensors
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) published reports in February that recommend approaches for testing low-cost, commercially available air sensors that detect particles with diameters of 10 microns or less (PM10) and other pollutants (nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, and sulfur dioxide). The reports supplement EPA reports published in 2021 that give guidance on sensors used to detect fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone. In addition to testing protocols, the reports provide target values to evaluate sensor performance and fillable templates for reporting testing results. The reports are intended to provide uniform guidance for use of sensors in non-regulatory monitoring applications, such as participatory science activities. While the testing protocols are voluntary, a consistent framework for testing sensors and reporting results will allow consumers to more easily compare different technologies and data from different sensors.
Submit Comments on NIEHS Draft Strategic Plan
Comments are being accepted on the NIEHS 2025-2029 draft strategic plan. NIEHS is seeking comments specifically on the following areas: research areas of emphasis, capacity and infrastructure priorities, scientific management and stewardship priorities, and crosscutting themes. Comments are due July 21 and can be submitted by email at [email protected].

PEPH Grantee Highlight
Jennifer Richmond-Bryant, Ph.D.
“If your work isn’t consistent with what the community is experiencing, then it doesn’t make sense to pursue. It’s our responsibility to support the communities that let us in and allow us to collect data,” said Jennifer Richmond-Bryant, Ph.D., an investigator with the NIEHS-funded Louisiana State University Superfund Research Program and co-investigator for the center’s Community Engagement Core. Her current research, which involves studying air pollution levels in Louisiana, was inspired by community concerns about the health effects of open burning at a hazardous waste thermal treatment plant in Colfax, Louisiana. Richmond-Bryant’s team presented their data to the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality, which then prohibited open burning at the treatment plant. The team will continue to monitor air quality to see how things change with the end of open burning.
Funding Opportunities
NOSI: Promoting Data Reuse for Health Research
Promotes data reuse and secondary data analysis to drive advancements in biomedical, behavioral, clinical, or health-related research. For this NOSI, applications must:
- Focus on advancing scientific inquiry and addressing pivotal health research questions via data reuse or secondary data analysis.
- Include data from at least one publicly accessible, NIH-funded data repository or knowledgebase.
- Describe how results and best practices for data reuse are to be shared with NIH and the broader community.
Deadlines: July 3, 2024; November 4, 2024
Hazardous Materials Worker Health and Safety Training (U45 Clinical Trials Not Allowed)
Supports the development of model programs for the training and education of workers engaged in activities related to hazardous materials and waste generation, removal, containment, transportation, and emergency response. The major objective of this funding opportunity is to prevent work-related harm by assisting in training workers on how best to identify and protect themselves and their communities from exposure to hazardous materials encountered during hazardous waste operations and transportation and environmental restoration of contaminated facilities or chemical emergency response.
Deadline: July 9, 2024
NIH Pathway to Independence Award (Parent K99/R00 Independent Basic Experimental Studies with Humans Required)
Helps postdoctoral researchers complete needed mentored training and transition to independent tenure-track or equivalent faculty positions. The K99/R00 award is intended to foster the development of an independent research program that will be competitive for subsequent independent funding and that will help advance the mission of NIH. Candidates must have no more than four years of postdoctoral research experience at the time of the initial or the subsequent resubmission or revision application. All applications submitted to this NOFO must propose basic science experimental studies involving humans. Prospective studies with humans conducted with specific applications toward processes or products in mind, including Food and Drug Administration Phase 0 or 1 studies, mechanistic clinical trials (e.g., those that examine the mechanisms by which an intervention works or the processes that account for an intervention's effects on clinical outcome), and safety and efficacy studies should submit under NIH Pathway to Independence Award (Parent K99/R00 Independent Clinical Trial Required). Observational studies involving humans should submit under NIH Pathway to Independence Award (Parent K99/R00 Independent Clinical Trial Not Allowed).
Deadlines: July 12, 2024; October 12, 2024
NIH Support for Conferences and Scientific Meetings (Parent R13 Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports high-quality scientific conferences that are relevant to NIH's mission and to public health. A conference is defined as a symposium, seminar, workshop, or any other organized and formal meeting, whether conducted face-to-face or via the internet, where individuals meet for the primary purpose of exchanging technical information and views or exploring or clarifying a defined subject, problem, or area of knowledge, whether or not a published report results from such meeting. NIH encourages conference grant applicants to enhance diversity by increasing the participation of individuals from diverse backgrounds, including those from underrepresented groups, in the planning, implementation, and participation in the proposed conference. Eligible organizations include higher education institutions, nonprofits, for-profit organizations, local government (including Indian/Native American Tribal Governments), federal government, and other organizations such as faith-based or community-based organizations.
Deadlines: August 12, 2024; December 12, 2024
Support for Research Excellence (SuRE) Award (R16 Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports research capacity building at institutions that award baccalaureate and/or graduate degrees in biomedical sciences and receive limited NIH Research Project Grant funding. SuRE-supported projects must have student participation in the execution, analysis, and reporting of the research. An applicant institution must demonstrate a commitment to build its research capacity and support for the program director/principal investigator of the award. This funding opportunity requires a Plan for Enhancing Diverse Perspectives (PEDP) as described in NOT-MH-21-310, submitted as Other Project Information as an attachment (see Section IV). Applications submitted to this funding opportunity for consideration by NIEHS must have a research focus on exposure-health-related responses from environmental agents within the mission interest of NIEHS (e.g., industrial chemicals or manufacturing byproducts, metals, pesticides, herbicides, air pollutants and other inhaled toxicants, particulates or fibers, fungal, and bacterial or biologically derived toxins). The Support for Research Excellence – First Independent Research (SuRE-First) Award (R16 - Clinical Trial Not Allowed) is also open. The purpose of this funding opportunity is to support faculty investigators who have not had prior independent external research grants, to furnish students with high-quality undergraduate and/or graduate research experiences and to enhance the institutional scientific research culture.
Deadlines: September 27, 2024; May 28, 2025
Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
Supports research on interventions to improve health in Native American populations, including:
- Etiologic research that will directly inform intervention development or adaptations.
- Research that develops, adapts, or tests interventions for health promotion, prevention, treatment, or recovery.
- Where a sufficient body of knowledge on intervention efficacy exists, research on dissemination and implementation that develops and tests strategies to overcome barriers to the adoption, integration, scale-up, and sustainability of effective interventions.
The inclusion of Native American investigators serving on the study team or as the program director or principal investigator is strongly encouraged. This funding opportunity is part of the Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health initiative, which also includes Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health (R21 Clinical Trials Optional), and Intervention Research to Improve Native American Health (R34 Clinical Trial Optional). For the R01 and R21 funding mechanisms, NIEHS is interested in applications that focus on the development, adaptation, efficacy, effectiveness, implementation, or sustainability of culturally appropriate interventions to prevent or mitigate the health impacts of environmental exposures that disproportionately impact Native American populations. For the R34 funding mechanism, NIEHS is interested in applications that support the initial development of a culturally appropriate clinical trial or research project in preparation for health promotion or disease prevention interventions addressing the health impacts of environmental exposures that impact Native American populations.
Deadline: October 1, 2024
NOSI: Data Informed, Place-Based Community-Engaged Research to Advance Health Equity
This NOSI is meant to stimulate community-engaged research that leverages geospatial data to probe the influence of geographic factors on disease development and health outcomes. Its goal is to use place-based research to help advance health equity in different communities. Applicants must select the institute or center and associated Notice of Funding Opportunity (NOFO) to use for submission of an application in response to the NOSI. NIEHS is interested in applications that integrate place-based environmental data with other data types and sources (such as human behavior and time-activity patterns, environmental data collected by low-cost sensor networks or wearable technologies, biomonitoring data, and other molecular or clinical outcome data) to improve exposure estimates at both the community and individual level, to advance understanding of the effects of environmental exposures on health outcomes, and to inform prevention and intervention strategies. Applicants may apply through PA-20-185 or PA-20-195.
Deadline: October 5, 2024
Mentored Research Scientist Development Award (Parent K01 Independent Basic Experimental Studies With Humans Required)
Provides support and protected time (3 to 5 years) for an intensive, supervised career development experience in the biomedical, behavioral, or clinical sciences leading to research independence. All applications submitted to this funding opportunity must propose basic science experimental studies involving humans, otherwise referred to in NOT-OD-18-212 as “prospective basic science studies involving human participants,” that fall within the NIH definition of a clinical trial and also meet the definition of basic research. Companion funding opportunities are available for mentored research that is not categorized as a basic experimental study. The Mentored Research Scientist Development Award (Parent K01 - Independent Clinical Trial Not Allowed) supports research that does not involve leading an independent clinical trial, a clinical trial feasibility study, or an ancillary clinical trial, but applicants may propose a research experience in a clinical trial led by a mentor. The Mentored Research Scientist Development Award (Parent K01 - Independent Clinical Trial Required) supports applicants proposing to serve as the lead investigator of an independent clinical trial, a clinical trial feasibility study, or a separate ancillary study to an existing trial.
Deadline: October 12, 2024
Academic Research Enhancement Award (AREA) for Undergraduate-Focused Institutions (R15 Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports small scale research grants at institutions that do not receive substantial funding from NIH, with an emphasis on providing biomedical research experiences primarily for undergraduate students and enhancing the research environment at applicant institutions. The research project must involve undergraduate students, and the research team must be composed primarily of undergraduate students. Student involvement in research may include participating in the design of experiments and controls, collecting and analyzing data, performing and troubleshooting experiments, presenting at meetings, drafting journal articles, participating in lab meetings to discuss results and future experiments, and other activities. NIEHS requires that applications submitted to this funding opportunity have a research focus on exposure-health-related responses from environmental agents within the mission interest of NIEHS (e.g., industrial chemicals or manufacturing byproducts, metals, pesticides, herbicides, air pollutants and other inhaled toxicants, particulates or fibers, fungal, and bacterial or biologically derived toxins).
Deadline: October 25, 2024
Notice of Intent to Publish a Funding Opportunity Announcement for Environmental Health Disparities Centers (P50)
The National Institute of Minority Health and Health Disparities in partnership with NIEHS and the National Cancer Institute plans to publish the Environmental Health Disparities (EHD) Centers funding opportunity in Summer 2024. EHD Centers will conduct environmental health disparities and environmental justice research, engage in research capacity building, and provide training across diverse disciplines and backgrounds with a disease agnostic focus. The Centers program will be updated to align with recent executive order (EO 14096) focused on environmental justice. For this renewal the program will focus on the prevention and mitigation of adverse environmental exposures that disproportionately impact racial, ethnic, under resourced and underserved populations. Projects must focus on one or more NIH-designated health disparities populations within the US and its territories, specifically racial and ethnic minority and socioeconomically disadvantaged populations and with the intersection of persons with disabilities, sexual and gender minorities, and persons from rural and/or under resourced areas.
Anticipated Deadline: November 1, 2024
Environmental and Climate Justice Community Change Grants Program
EPA is accepting applications for its Environmental and Climate Justice Community Change Grants program. The program provides Inflation Reduction Act funds in environmental and climate justice activities to benefit disadvantaged communities through projects that reduce pollution, increase community climate resilience, and build community capacity to address environmental and climate justice challenges. These place-based investments will be focused on community-driven initiatives to be responsive to community and stakeholder input. The entities eligible to apply under this opportunity are:
- A partnership between two community-based nonprofit organizations.
- A partnership between a community-based nonprofit organization and one of the following:
- A federally recognized tribe.
- A local government.
- An institution of higher education.
Other organizations and entities may be able to participate and be involved in the Community Change Grants projects as collaborating subrecipients and/or procurement contractors selected in compliance with competition requirements. EPA is accepting applications on a rolling basis; therefore, interested applicants are encouraged to apply early. To apply for this opportunity, see the announcement on Grants.gov.
Deadline: November 21, 2024
Upcoming PEPH-related Events
Columbia Climate School: Extreme Heat Workshop (New York City, New York). Climate scientists, engineers, impact researchers, social scientists, and other interested public and private individuals will discuss emerging risks from extreme heat. Participants will assess the state of knowledge on heat hazards, identify community needs and research gaps, and discuss how to build societal resilience to extreme heat. This workshop is hosted by the Columbia Climate School and receives funding from both the National Science Foundation and Columbia Climate Center. The registration deadline was June 15.
NIH Community Engagement Alliance Consultative Resource Webinar: Ensuring Ethical Research in Our Communities – Navigating NIH Policy, Human Subjects and Data Protection Guidance, Data Sharing Requirements, and Community-Based Research Review Processes (webinar.) Participants in this webinar will learn about ethical considerations in research and how to protect human subjects data. NIH will also host office hours to further support webinar participants in understanding and applying the webinar’s content. The session is part of a series that supports community organizations in preparing research applications and implementing research studies. Registration for the webinar is available.
National Environmental Health Association’s Annual Educational Conference and Exhibition (Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania and virtual). This year’s theme is New Horizons: Building Bridges to Shape the Environmental Health Future. The conference will have educational sessions on topics such as air quality, climate change, heat waves, data modernization, and artificial intelligence for environmental health. You can view the conference agenda. Registration for the conference is available (including single-day options).
Environmental Protection Agency’s National Environmental Justice Community Engagement Call (virtual). The Environmental Protection Agency hosts regular community engagement calls to inform the public about EPA’s environmental justice work and maintain an ongoing dialogue with environmental justice advocates. Registration for the engagement call is encouraged but not required and is not yet open.
EPA Research Webinar Series: Impacts of Extreme Precipitation and the Urban Heat Island (webinar). This webinar is part of the EPA’s series about air, climate, and energy research. Presenters will talk about their research on air quality, the impacts of air pollution and climate change, environmental justice, responses to impacts of climate change, and other pollution-related risks. Registration for the webinar on precipitation and the urban heat island is available.
NIH Community Engagement Alliance Consultative Resource Webinar: Moving From Action to Knowledge - Using Research to Change Policy and Practice. Participants in this webinar will learn how to use research findings to create social change. NIH will also host office hours to further support webinar participants in understanding and applying webinar content. The session is part of a series designed to support community organizations in preparing research applications and implementing research studies.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health: Environmental Justice and Environmental Health Disparities (Boston, Massachusetts and virtual). This intensive workshop will cover exposure assessment techniques and community engagement and health policy applications in support of solution-driven environmental justice research. The focus of this workshop is to provide training in environmental justice research to environmental health scientists. It will include lectures and hands-on learning experiences. Registration for the Environmental Justice workshop is available. This workshop is part of a series, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health: Skills for Health and Research Professionals Program, designed for health and research professionals at all career stages and focuses on providing practical skills.
EPA Research Webinar Series: Air Pollution Impacts on Reproductive and Mental Health (webinar). This webinar is part of the EPA’s series about air, climate, and energy research. Presenters will talk about their research on air quality, the impacts of air pollution and climate change, environmental justice, responses to impacts of climate change, and other pollution-related risks to the environment. Registration for this webinar is not yet available.
International Society for Environmental Epidemiology Annual Meeting: Addressing Challenges in Environmental Health, Justice, and Development (Santiago, Chile). Topics will include air pollution, the built environment, climate, exposures and exposure assessment methods, policy, and water pollution. Registration for the annual meeting is now open.
International Society of Exposure Science Annual Meeting: Exposures that Impact Health in Vulnerable Populations. (Montreal, Quebec). Participants will hear about research in exposure science, epidemiology, toxicology, and risk assessments. The meeting will bring together participants from academia, government, and nonprofit organizations. Registration for the annual meeting is available.
American Public Health Association (APHA) 2024 Annual Meeting and Expo (Minneapolis, Minnesota). The theme of the annual APHA meeting is Building Trust in Public Health and Science. The meeting will include a session on report-back as well as poster sessions and opportunities for networking. Registration for the APHA meeting and expo is open.








