Oceans and Human Health Researchers Adopt Community Engagement Framework
Researchers from the Centers for Oceans and Human Health (COHH) created a strategic framework for community engagement in research on oceans and human health. Community engagement is a beneficial component of public health research that supports effective and efficient solutions to health problems, builds trust, and helps translate research results back to communities. Oceans and human health research can benefit from community engagement, and efforts are being made to incorporate it further. In an April 2022 paper , the authors describe the framework, explain why it was created, and emphasize the importance of bringing community engagement into this type of research.
Community Engagement in the Work of the Centers for Oceans and Human Health
The NIEHS- and National Science Foundation-funded COHH program includes four centers:
- Center for Oceans and Human Health and Climate Change Interactions, led by the University of South Carolina.
- Great Lakes Center for Fresh Waters and Human Health at Bowling Green State University.
- Greater Caribbean Center for Ciguatera Research at the Florida Gulf Coast University.
- Woods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
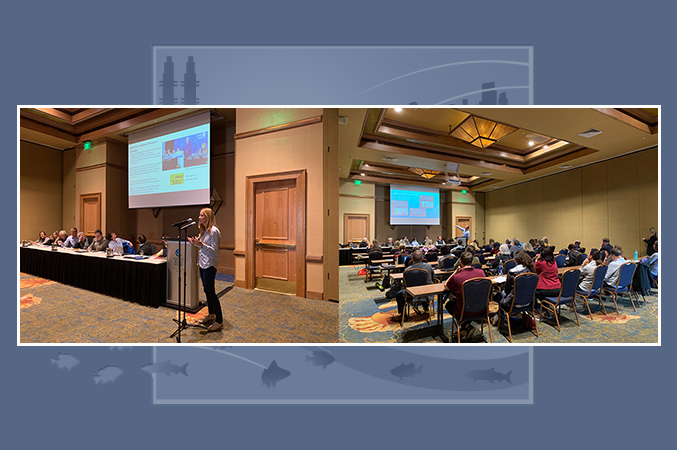

Presentations at a workshop on “Communicating Harmful Algal Blooms Science,” convened by Woods Hole Center for Oceans and Human Health CEC Director Mindy Richlen at the 2019 Symposium for Harmful Algal Blooms in the U.S. (Photos courtesy of Mindy Richlen)
These centers address an array of topics related to oceans and human health, including public health concerns related to oceans and other bodies of water. Areas of interest include harmful algal blooms and how exposure affects human health, the effects of climate change on aquatic pathogens, microplastics, and environmental justice efforts.
In 2019, NIEHS and the National Science Foundation directed each COHH to create a Community Engagement Core (CEC), like other NIEHS-funded center programs. At the 2019 COHH annual meeting, the CECs established a collaborative working group that developed a community engagement plan, which later became the Strategic Framework for Oceans and Human Health Community Outreach and Engagement.
“Research translation and community engagement are vital to NIEHS’ portfolio of research,” stated Anika Dzierlenga, Ph.D., NIEHS program director of the COHH. “This framework will support the COHH Community Engagement Core and others in determining effective engagement strategies.”
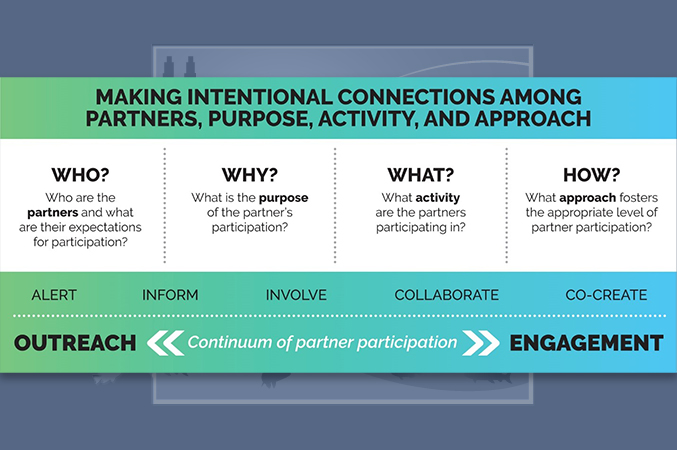
The Strategic Framework for Oceans and Human Health Community Outreach and Engagement, modified from the International Association for Public Participation’s spectrum of public participation. (Figure courtesy of Margaret Carson, Diane Doberneck, Zac Hart, Heath Kelsey, Jennifer Pierce, Dwayne Porter, Mindy Richlen, Louisa Schandera, and Heather Triezenberg)
Ocean and human health researchers who use the framework are encouraged to answer questions that will help them make intentional connections with community members. Answers to these questions will determine four important aspects of community engagement:
- Knowing who the partners will be.
- Identifying the purpose of partners’ participation.
- Designing the activity in which the partners will participate.
- Implementing the approach that will foster the level of participation appropriate for the partners.
The framework recognizes that there can be varying degrees of community engagement in any project. This continuum allows for designing activities along the spectrum of outreach and engagement efforts. The spectrum encompasses projects with minimal community participation in which researchers alert or inform community members of research activities or results, projects with more community involvement in which public concerns are considered, and projects in which the community is included as collaborators.
The community engagement team and researchers adapted the framework from an existing one by the International Association for Public Participation . Key changes include modifying the community engagement continuum, for example by reflecting the community-based participatory research principle of co-creation, which is when researchers and partners have equal say in developing and analyzing research, and centering community partners through the framework’s questions that determine partner involvement.
“Identifying partners is critical to our work,” said Mindy Richlen, Ph.D., director of the Woods Hole Center’s CEC. “Being specific about who is engaged and how helps to identify target audiences and partners, focus the research on what matters to the community, and achieve shared goals and outcomes.”
Using the Framework
The publication provides several case studies to illustrate how the framework ties into levels of engagement.
One case study describes how COHH researchers and partners developed educational materials for K-12 students related to oceans and human health. Partners engaged at the levels of “inform” and “involve.” For this project, a science educator helped develop the materials, and K-12 teachers and students participated in classroom testing to evaluate the materials. As a result, students learned about harmful algal blooms, which improved their ocean literacy. The activities specified tactile teaching aids to facilitate participation by students with visual impairments, including 3D printed models of several harmful algal bloom species, raised-line drawings and graphs for data interpretation, and braille captioning.
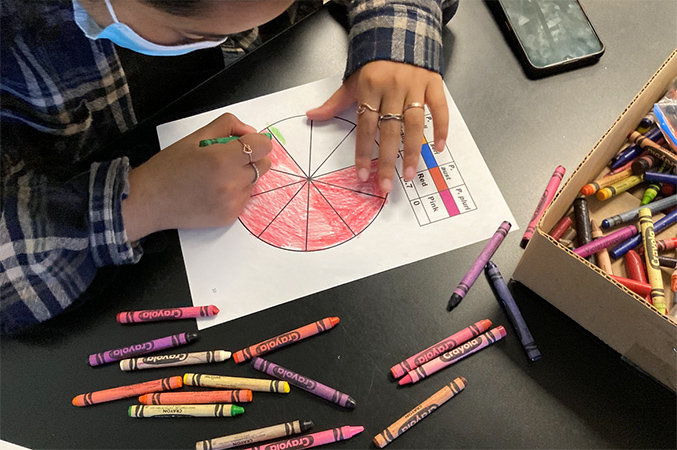

Using the materials developed by COHH researchers and partners, a K-12 student colors in the slices of a pie graph that represent the abundance of different harmful algal bloom species. (Photo courtesy of Mindy Richlen)
In another case study, authors described the importance of partner participation, as exemplified by an University of South Carolina team’s efforts to address environmental justice concerns in areas of Charleston, South Carolina (described in the January 2023 PEPH newsletter). These ongoing advocacy efforts aim to ensure that community voices are heard in Charleston’s flood adaptation planning.
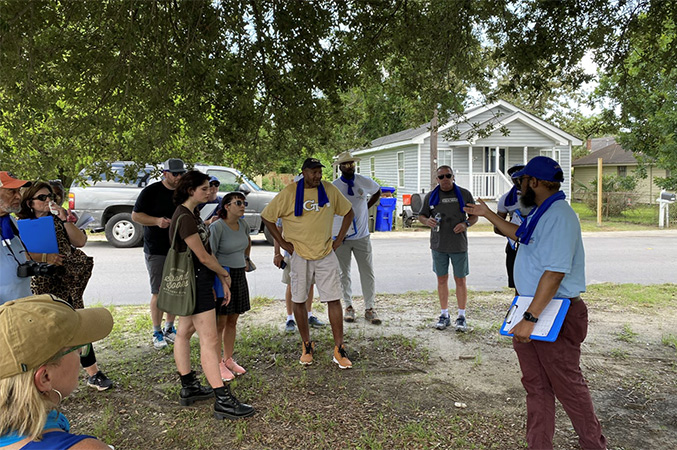

Participants in the Charleston, South Carolina, Rosemont Field Practicum in July 2022 observing areas of environmental concern in a local neighborhood. (Photo courtesy of Dwayne Porter, CEC lead for the Center for Oceans and Human Health and Climate Change Interactions at the University of South Carolina)
Notably, after creating the framework, COHH teams evaluated their existing projects against the framework and determined that projects involving the ‘co-create’ level of engagement were lacking. Moving forward, they aim to identify more opportunities to support co-creation with community partners.
“We believe this framework will foster community engagement in oceans and human health research, such as responding to public health concerns regarding the growing impacts of climate change,” reflected Richlen. “Researchers can use the framework for a more systematic approach to engaging with communities to address critical public health issues at the intersections of oceans and water systems and human health.”
Federal Agencies Urge Local Governments to Remediate Lead in Early Care and Education Settings
In March, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services issued a joint letter encouraging state and local governments to use federal funding to reduce and remove potential lead exposure sources in settings where children spend a significant amount of time, such as elementary schools and child care centers. The agencies co-chair the President’s Task Force on Environmental Health Risks and Safety Risks to Children, and the letter is part of their collaborative efforts to reduce children’s exposure to lead. Children are especially vulnerable to the effects of lead because they are still developing. The letter describes the White House’s Lead Pipe and Paint Action Plan, which encourages federal, state, and local governments to replace lead pipes and remediate lead pipes. It also describes the health effects of lead on children, such as learning problems and anemia, and the federal funding sources available for remediating lead in settings where children spend significant time.
National Academy of Medicine Now Forming Climate Communities Network
The National Academy of Medicine is creating a Climate Communities Network and is accepting applications until June 23 for community leaders to join as members. The network will bring together leaders who work in communities disproportionately impacted by climate change in order to elevate community expertise and efforts. Members will build a community of practice with other members, strategic partners (such as invited representatives from academia, government, industry, and philanthropy), National Academy of Medicine staff, and other experts, and will catalyze innovation, inform policy, drive funding, and co-design solutions. The network will be part of the National Academy of Medicine’s Climate Grand Challenge, which strives to improve and protect human health by transforming systems that contribute to and are impacted by climate change. You can join the listserv for the Climate Grand Challenge.
NIEHS-funded Researchers Find Link Between Air Pollution Exposure and Dementia
In a paper published in April, NIEHS-funded researchers demonstrated a link between exposure to fine particulate air pollutants and the risk of developing dementia. In their systematic review and meta-analysis, the authors used the Risk of Bias in Non-Randomized Studies of Exposure tool, which provides a method for assessing the risk of bias in observational epidemiological studies. Using the tool allowed the authors to thoroughly examine the strength of evidence about the potential effect of pollution on the risk of dementia. Most of the studies included in the meta-analysis were about fine particulate air pollutants (PM2.5), while some studies were about nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen oxide. The analysis showed consistent evidence of an association between PM2.5 exposure and dementia, even when annual exposure levels were lower than standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
White House Releases Executive Order on Environmental Justice
The White House released an Executive Order to Revitalize Our Nation’s Commitment to Environmental Justice for All on April 21. The executive order directs federal agencies to incorporate environmental justice (EJ) into their work and establishes a White House Office of Environmental Justice to implement policies across the federal government. Agencies are also directed to assess their EJ efforts and develop strategic plans and assessments that will be published through the EJ Scorecard, a tool established by the Executive Order. The scorecard currently shows actions taken by federal agencies from 2021 to 2022 to advance the Justice40 Initiative, implement and enforce environmental and civil rights laws, and embed EJ throughout the federal government. For example, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Scorecard shows that it supports 13 Justice40 programs and has released 18 funding announcements covered by the initiative. HHS has embedded EJ in its policies and decision-making through staff training, the creation of 25 tools or resources, and by conducting community engagement. Read more about the executive order by reviewing the fact sheet.

PEPH Grantee Highlight
Allison Patton, Ph.D.
By tracking pollution in the environment, Allison Patton, Ph.D., works to improve the health of communities. She began working on traffic-related air pollution while at Tufts University through her involvement with the Community Assessment of Freeway Exposure and Health Study, a community-based participatory research project that maps air pollution and engages the community to respond to health concerns. You can read more about the study in the July 2021 PEPH newsletter. Patton currently works at the Health Effects Institute where she applies her background in research on air pollution to answer questions from policymakers about issues such as non-exhaust emissions from breakdown of car and road components.
Funding Opportunities
Research to Action: Assessing and Addressing Community Exposures to Environmental Contaminants (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
Encourages multidisciplinary projects to investigate the potential health risks of environmental exposures of concern to a community and to implement an environmental public health action plan based on research findings. Projects supported under this program are expected to employ community-engaged research methods to not only conduct research but also to seamlessly translate research findings into public health action. Check out the Research to Action Currently Funded Grantees webpage for a sense of the types of projects supported through this FOA.
Deadline: January 21, 2020
Research With Activities Related to Diversity (ReWARD) (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
ReWARD funding will support research in areas related to the programmatic interests of NIEHS and ongoing diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility activities focused on enhancing diversity in the biomedical research enterprise within the U.S. and territories. This funding is intended for individuals with no current NIH research project grant funding at the time of the award. This announcement requires a Plan for Enhancing Diverse Perspectives as part of the application.
Deadlines: June 5, 2023; October 5, 2023; February 5, 2024
Strategies for Responsibly Reporting Back Environmental Health and Non-Genomic Research Results (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
NIEHS, in partnership with the NIH Office of Science Policy, the All of Us Research Program, and the National Human Genome Research Institute, seeks applications that will identify, develop and/or adapt, as well as test strategies for responsibly reporting back environmental health, non-genomic research, and gene-environment interaction results to research participants and/or key partners (for example, health care professionals, IRBs, and policy makers). Applications are encouraged to address at least two of the specific themes of research interest, which include:
Applicants are strongly encouraged to partner with partner with one or more community-based organizations and/or an appropriate key partner group.
Deadline: June 15, 2023
Notice of Special Interest (NOSI): EXposome in Autoimmune Disease Collaborating Teams PLANning Awards (EXACT-PLAN) (Clinical Trials Not Allowed)
Invites applications for exploratory, early, and conceptual stage research projects aimed at the design, development, and implementation of a future national, interdisciplinary, collaborative, team science research network that will advance the study of the exposome in autoimmune diseases (Exposome in Autoimmune Diseases Collaborating Teams, EXACT). The future EXACT Network will conduct research to discover the environmental exposures that influence disease susceptibility, onset, and outcomes and will develop a systems-level approach to understanding the mechanisms underlying how exposures perturb cellular, organ, and tissue function across autoimmune diseases. The exploratory, developmental grants requested under this announcement are intended to enable institutions to plan research strategies; develop partnerships, infrastructure, and capabilities needed to address the major goals of a future collaborative EXACT network; and develop a research framework and strategies to support coordination among studies, collaborative research projects, and sites. Applications for this initiative must be submitted under PA-20-195.
Deadline: June 16, 2023
Emergency Award: Novel Insights through Cross-Site Analyses of Existing RADx-®UP Data (R21 Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports new exploratory/developmental grants for analysis of existing data collected within the Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics – Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) consortium. Successful applications will leverage common demographics and other data from a minimum of three sites (with geographic diversity; inclusion of a greater number of sites is encouraged) to ask important questions around COVID-19 testing access and uptake. Applications that address factors affecting COVID-19 testing and related COVID-19 outcomes, specific COVID-19 response, intervention approaches within and across populations, and other novel questions are encouraged. Research objectives include but are not limited to community-engaged interventions to address stigma, bias, distrust and fear; and psychosocial, behavioral, and ethical factors driving COVID-19 testing and vaccination.
Deadline: July 3, 2023
Emergency Award: RADx-®UP Dissemination and Implementation Research on COVID-19 Testing Interventions among Underserved and Vulnerable Populations (R01 Clinical Trial Optional)
The Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics – Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) initiative seeks to address COVID-19 morbidity and mortality disparities among underserved and vulnerable populations with disproportionate rates of SARS-CoV-2 and/or undue COVID-19 burden by understanding strategies and interventions to increase testing access, acceptability, and uptake. As testing protocols and requirements have evolved and become less common, this funding opportunity will support dissemination and implementation research on how evidence-based practices, interventions, and policies are effectively translated to and used in real-world settings such as residential care facilities and other congregate settings, clinical settings, schools, rural areas, and remote communities. These new projects will expand the evaluation of the effectiveness of COVID-19 interventions with a focus on sustainability. This is important given that the end of the COVID-19 national emergency and public health emergency declarations on May 11 may affect the implementation of evidence-based COVID-19 testing interventions. The overarching goal is to ensure that successful interventions in the RADx-UP and other programs carry forward to dissemination and implementation.
Deadline: July 10, 2023
SBIR E-Learning for Hazardous Materials (HAZMAT) and Emergency Response (R43/R44 Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
Supports the development of e-Learning health and safety training products from a variety of delivery methods to assist both students and instructors in the training and education process. Note that all products must be directly related to the health and safety training of workers exposed to hazardous materials. NIEHS encourages applicants to review the SBIR E-Learning for HAZMAT Program, to pursue partnerships and collaboration with NIEHS Worker Training Program awardees, and to design new technology-enhanced training methods or e-Learning products that can enhance the existing NIEHS-supported curricula and training programs while adhering to the Minimum Health and Safety Training Criteria: Guidance for Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) and HAZWOPER-Supporting Training.
Deadline: July 14, 2023
Lasker Clinical Research Scholars Program (Si2/R00 Clinical Trial Optional)
The Lasker Clinical Research Scholars program will offer applicants the opportunity to compete for a unique combination of intramural and extramural resources for clinical research. The program will support a small number of exceptional clinical researchers in the early stages of their independent careers to promote their development as fully independent scientists. The program combines a period of research experience as a tenure-track investigator in the Intramural Research Program with additional years of independent financial support, either within the Intramural Research Program or at an extramural research institution. Successful applicants will receive support in two phases: 1) support for scholars in the Intramural Research Program for up to 5 years, with the possibility of an extension for an additional 2 years; and 2) either continued Intramural Research Program support, or up to 3 years of support to continue research as an independent clinician scientist at an extramural institution.
Deadline: June 24, 2022
STrengthening Research Opportunities for NIH Grants (STRONG): Structured Institutional Needs Assessment and Action Plan Development for Resource Limited Institutions (RLIs) (UC2 - Clinical Trial Not Allowed)
The STRONG-RLI program will support research capacity needs assessments by eligible RLIs. The program will also support recipient institutions in using the results of the assessments to develop action plans for how to meet the identified needs. The program’s goal is to increase competitiveness in the biomedical research enterprise and foster institutional environments conducive to research career development. Awards are intended to support RLIs in analyzing their institutional research capacity needs and strengths. RLIs are defined for this funding opportunity as institutions with a mission to serve historically underrepresented populations in biomedical research that award degrees in the health professions or the sciences related to health, in STEM fields including social and behavioral sciences, and have received up to $25 million (total costs) per year of NIH research project grant support for the past three fiscal years.
Deadline: September 18, 2023
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award Institutional Research Training Grant (Parent T32)
Supports development of and/or enhances research training opportunities for individuals interested in careers in biomedical, behavioral or social sciences, clinical research, health services research, or in any other research discipline related to the NIH mission. The NIH Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) program helps ensure a diverse pool of highly trained scientists is available in appropriate scientific disciplines to address the nation's biomedical, behavioral, and clinical research needs. To accomplish this goal, NRSA training programs are designed to train individuals to conduct research and to prepare for research careers. More information about NRSA programs may be found at the Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA website.
Deadline: September 25, 2023
Limited Competition: Superfund Hazardous Substance Research and Training Program (P42 Clinical Trial Optional)
NIEHS is announcing the continuation of the Superfund Hazardous Substance Research and Training Program, referred to as Superfund Research Program (SRP) centers. SRP center grants will support problem-based, solution-oriented research centers that consist of multiple, integrated projects representing both the biomedical and environmental science and engineering disciplines; as well as cores tasked with administrative (which includes research translation), data management and analysis, community engagement, research experience and training coordination, and research support functions. Collectively, the center's research projects (maximum of six) should represent a range of basic and applied research that contributes to the problem-based, solution-oriented goal of the center. Each center's central problem should be addressed by the contributions of these projects and each project should have the necessary biomedical and/or environmental science and/or engineering expertise to address the central problem.
Deadline: October 2, 2023
Addressing the Impact of Structural Racism and Discrimination on Minority Health and Health Disparities (R01 - Clinical Trial Optional)
Supports intervention research to address the impact of structural racism and discrimination on minority health and health disparities. Research projects must address structural racism and discrimination in one or more NIH-designated populations with health disparities in the U.S. and should address documented disparities in health outcomes. Applications are also expected to provide a conceptual model identifying hypothesized pathways between the structural racism and discrimination and health outcomes. NIEHS is interested in applications that are within scope of its 2018-2023 Strategic Plan, meet the criteria established in this FOA, and focus on intervention research that mitigates or prevents the impacts of environmental exposures on communities due to structural racism and discrimination. Applicants are strongly encouraged to utilize community-engaged research approaches that ensure equity, such as including community partners as part of the research team and having letters of support from community partners. Applications that demonstrate collaborative (i.e., community-academic partnerships) intervention approaches to address the negative health effects of structural racism and discrimination across multiple populations with environmental health disparities will be prioritized.
Deadlines: March 24, 2023; October 10, 2023









